Wind and solar need cheap, long-duration storage to even out its inherent weather-determined intermittency. Deborah Halber, writing for MIT News, describes the development of iron-air batteries. Iron is cheap and available worldwide. Storage duration is multi-day. They are much heavier and take up more space than lithium-ion batteries, but that doesn’t matter for immobile grid storage. The target price tag of $20/kWh (one-tenth the cost of … [Read more...]
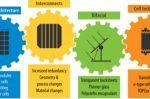
Solar PV technology improvements are rapid. But how do you test the long-term reliability of the new designs?
Solar PV module technology moves fast, and is delivering improvements continuously. So fast that it’s no trivial matter to judge the long-term reliability of the changes. It’s a crucial issue as modules, once deployed, are expected to deliver results over lifetimes that span decades. Sara Fall and Jarett Zuboy at NREL describes a process designed to identify and address potential reliability problems quickly, before they are observed in the … [Read more...]
Research into how electrons and protons couple at an electrode can create more efficient fuel cells, electrolysers
Every efficiency gain discovered in the lab feeds through to the final cost of electricity. Anne Trafton at MIT describes new research looking at how electrons and protons couple at an electrode surface, which drives electric current. It’s a critical step in many energy technologies, including fuel cells, hydrogen electrolysers, batteries, and CO2 conversion into chemical fuels. The first step was to develop a way to design electrode surfaces … [Read more...]
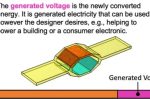
Electrostatic Generator fabrics can capture energy from cars depressing roads, swaying buildings + more
Literally anything that moves is using energy that can be harnessed. Not just waves rolling toward shore but cars depressing roads, buildings swaying in the wind, and much more. One way to harness it is to create a material that can be woven into the fabric of roads and buildings so that it captures the energy and converts it into electricity. Caitlin McDermott-Murphy at NREL describes research into Hexagonal Distributed Embedded Energy … [Read more...]
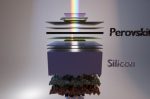
Tandem solar cells (perovskite + silicon) can reach 40% energy conversion rates
Tandem solar lays new perovskite cells over standard silicon cells. Perovskite absorbs the shorter wavelengths of light that silicon misses. So the thin layer of perovskite collects the visible wavelengths, and lets the near-infrared light through to the silicon underneath. Martina Grünwald and Sarah Michaud writing for the WEF point at the results of R&D and demonstrations in Germany, Switzerland, Saudi Arabia and China. Energy conversion … [Read more...]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 46
- Next Page »