Zach Winn at MIT describes a new method of building high-temperature concentrated solar power systems. The solar receiver heats air to around 1,000°C at atmospheric pressure. The system circulates the hot air with no combustion or emissions to drive a turbine. The system can deliver daytime power and overnight thermal energy storage to provide round-the-clock power. More interestingly, it can provide industrial-grade heat. It’s being … [Read more...]
A global review of Battery Storage: the fastest growing clean energy technology today
The IEA report “Batteries and Secure Energy Transitions” looks at the impressive global progress, future projections, and risks for batteries across all applications. 2023 saw deployment in the power sector more than double. Strong growth occurred for utility-scale batteries, behind-the-meter, mini-grids, solar home systems, and EVs. Lithium-ion batteries dominate overwhelmingly due to continued cost reductions and performance improvements. And … [Read more...]
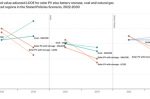
Iron-air batteries: long-duration grid storage targets 1/10th the cost of lithium-ion
Wind and solar need cheap, long-duration storage to even out its inherent weather-determined intermittency. Deborah Halber, writing for MIT News, describes the development of iron-air batteries. Iron is cheap and available worldwide. Storage duration is multi-day. They are much heavier and take up more space than lithium-ion batteries, but that doesn’t matter for immobile grid storage. The target price tag of $20/kWh (one-tenth the cost of … [Read more...]
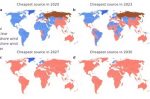
New Solar study: 50% of global power by 2050, even without more ambitious climate policies
Nadia Ameli at UCL and Femke Nijsse and Jean-Francois Mercure at the University of Exeter present their study that shows solar is on track to make up more than half of global electricity generation by 2050, even without more ambitious climate policies. This far exceeds any previous estimates: last year’s IEA World Energy Outlook predicted that solar would account for only 25% by 2050. The authors’ macroeconomic model takes the latest … [Read more...]
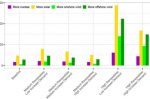
Health benefits of Wind Power: first replace the most polluting fossil plants, not the most expensive
It makes economic sense, when intermittent wind (or solar) generation rises, to turn down the most expensive fossil plants. Or does it? Join the dots to health costs and it may make more economic sense to turn down the most polluting plants first. Jennifer Chu at MIT describes research there that creates models and scenarios to interrogate that theory. Using hourly generation records, pollution and health cost data from across the U.S. they found … [Read more...]
Reversible Hydrogen fuel cells: can H2 gas-to-power support the grid economically?
We know about making green hydrogen from excess intermittent wind and solar. We also know that that same intermittency means the gaps in wind and solar generation need filling. Green hydrogen is very expensive to make. But what if that green hydrogen could be economically converted back to power when needed? Writing for Stanford University, Edmund Andrews describes new research, in collaboration with the University of Mannheim in Germany, into … [Read more...]
Electricity markets with high shares of Wind and Solar will need Nuclear
When electricity markets have high shares of wind and solar – the goal of many regions around the world – is it more efficient to build a nuclear power plant instead of investing further in more renewable capacity? The answer is yes, according to a study by Machiel Mulder, Xinyu Li and Arjen Veenstra at the University of Groningen. In essence, it’s because nuclear benefits from the high (scarcity) prices when there’s little wind or sunshine. Here … [Read more...]
Solar + Storage Hybrid plants are poised for explosive growth in the U.S.
At the beginning of 2021 the U.S. had 73 solar and 16 wind hybrid projects, amounting to 2.5GW of generation and 0.45GW of storage. By the end of 2021, over a third of the 675GW of solar in the grid connection queue were hybrids, and 19GW were wind hybrids. Only one in four typically get approved, built and connected. But that still points at a twenty-five-fold increase in hybrid generation. It’s why Joachim Seel, Ben Paulos and Will Gorman at … [Read more...]
Lifting and lowering tons of bricks: the best storage solution for Wind and Solar intermittency?
It’s a high capacity storage system that’s simplicity itself. Use excess wind and solar to raise heavy weights. Keep them at a height for as long as you like. Lower them to generate electricity. James Conca looks at a system being developed by Energy Vault and already being demonstrated in the Swiss national grid. At scale, a single “vault” with 10,000 bricks will have an annual output of 27 GWh, sitting on only 14 acres of land. The bricks are … [Read more...]
Improving grid response to support climate targets and increased renewables [Energy Post event video]
We present our video of the online discussion from February 24, 2021 on smartgrid response. Digital, automated, data-driven smart response systems can play a key role in grid security and stability going forward. This makes asset monitoring and controllability - underpinned by the Smart Grid Indicator which is now part of the EU Electricity Directive (Article 59) - a vital link in the chain. Taking part were Vera Silva, COT, General Electric and … [Read more...]
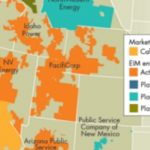
Creating a market to trade excess wind/solar between states (without outsourcing your emissions!)
How do you get neighbouring states, with different renewables mixes, and different emissions targets and penalties, to trade their surplus energy? It’s one of the biggest challenges to face the rapid growth of intermittent wind and solar. Meredith Fowlie at the Energy Institute at Haas describes how an “Energy Imbalance Market” (EIM) is operating across eight states in the west of the U.S. Bidding for your neighbour’s excess renewable energy is … [Read more...]
Wind Farm “wake steering”: small re-alignments of turbines can increase output by 40%
The wake from one wind turbine makes the turbines behind it less efficient. It’s similar to the way a speedboat is slowed by the choppy water caused by the boat in front. Vincent Xia reports on how scientists at Stanford University have been testing ways of fine-tuning the alignment of turbine arrays to reduce turbulence and increase output. The biggest wins (a 47% increase) are at low wind speeds, when turbines can otherwise stop altogether. At … [Read more...]
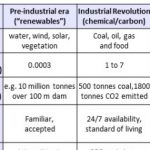
Climate Change and the Third Energy Revolution
The anxiety expressed by young people today about Climate Change is reasonable, but they offer no thought-out solution. We should examine the available scientific options in a form accessible to those without specialised knowledge and starting from what natural science has to say about energy and where to find it. (In this article precision is set aside to allow the science underlying the orders of magnitude to be clear and simple.) … [Read more...]
Solar intermittency: upbeat “annual” carbon reduction estimates miss the “hourly” reality
There is a maximum speed at which solar capacity can expand. You know you’ve passed it when insufficient storage means solar curtailment, or selling the daytime excess means curtailment of other clean energy generators. As solar grows, so too will this problem. Vincent Xia, at the Precourt Institute for Energy, Stanford University, reports on a new Stanford study which says emissions predictions are not taking this into account, thus … [Read more...]
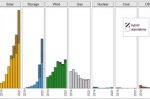
Barriers to intermittent renewables and battery storage come tumbling down
The astonishing growth of the renewable energy sector shows little sign of slowing, as costs continue to plummet, along with the cost of energy storage, to remove many of the barriers to using intermittent renewable generating sources in a range of applications. Much of this is down to the fact that the cost of battery energy storage is one third lower than this time last year. … [Read more...]