After good progress globally since 2015, basic energy access reversed in recent years for the first time in a decade, says the IEA. The 2024 edition of “Tracking SDG 7: The Energy Progress Report” measures progress on “strategic development goals” that include universal access to electricity and clean cooking, doubling historic levels of efficiency improvements, and substantially increasing the share of renewables in the global energy mix. The … [Read more...]
The Fossil Fuel system wastes 2/3rds of its energy before it gets to you. Inefficiency is driving it out (not just emissions)
Today’s fossil energy system is very inefficient: almost two-thirds of all primary energy is wasted in energy production, transportation, and use, before fossil fuel has done any work or produced any benefit. That’s almost 400 EJ wasted, worth over $4.5tn, or almost 5% of global GDP. Two activities - fossil fuel power plants and internal combustion engines - are responsible for almost half the energy waste globally. Daan Walter, Kingsmill Bond, … [Read more...]
Are the prospects for Small Modular Reactors being exaggerated? Five key characteristics examined
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) are being presented as the next generation of nuclear technology. While traditional plants face cost overruns and safety issues, SMRs are seen by their champions as cheaper, safer, and faster to deploy. But Ed Lyman at UCS cites evidence that cast these claims into doubt. In five sections of this article, he lists the reasons why. SMRs are not more economical than large reactors. SMRs are not generally safer or more … [Read more...]
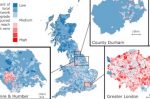
Upgrade the grid, or avoid by incentivising flexibility? Electricity demand mapping can tell you what to do
Power grids across the world need upgrading to accommodate the rapidly rising amount of electricity being generated. Without it, it is a serious bottleneck to the transition to clean fuels. Sheridan Few at the University of Leeds summarises his co-authored study that creates a map of where upgrades are most needed in the UK. The map’s purpose is twofold. Firstly, it predicts where power consumption will rise the most and the upgrades are … [Read more...]
Research into how electrons and protons couple at an electrode can create more efficient fuel cells, electrolysers
Every efficiency gain discovered in the lab feeds through to the final cost of electricity. Anne Trafton at MIT describes new research looking at how electrons and protons couple at an electrode surface, which drives electric current. It’s a critical step in many energy technologies, including fuel cells, hydrogen electrolysers, batteries, and CO2 conversion into chemical fuels. The first step was to develop a way to design electrode surfaces … [Read more...]
Batteries are still getting exponentially cheaper, more efficient: ready to displace half of global fossil fuel demand by 2045?
A new report by RMI says batteries are on the path to replace 175 EJ of fossil fuel demand in the power sector, 86 EJ of fossil fuels from road transport and can put at risk another 23 EJ from shipping and aviation. That equates to a phaseout of half of global fossil fuel demand in the next two decades. Daan Walter, Sam Butler-Sloss and Kingsmill Bond at RMI summarise the findings in six graphs with explanations. Battery sales are growing … [Read more...]
The link between global GDP growth and CO2 emissions is weakening rapidly. Will emissions peak well before 2030?
Economic growth has been closely tied to rising greenhouse gas emissions since the industrial age. But data now clearly shows that that GDP growth and CO2 emissions are diverging. Siddharth Singh at the IEA presents the numbers. In advanced economies that divergence now seems locked in, with 2007 marking the moment of peak emissions (and not simply because of offshoring manufacturing). Even in developing economies GDP growth is far outpacing … [Read more...]
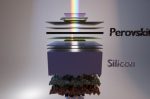
Tandem solar cells (perovskite + silicon) can reach 40% energy conversion rates
Tandem solar lays new perovskite cells over standard silicon cells. Perovskite absorbs the shorter wavelengths of light that silicon misses. So the thin layer of perovskite collects the visible wavelengths, and lets the near-infrared light through to the silicon underneath. Martina Grünwald and Sarah Michaud writing for the WEF point at the results of R&D and demonstrations in Germany, Switzerland, Saudi Arabia and China. Energy conversion … [Read more...]
Chemicals Industry needs Sustainable Feedstocks to complete their net-zero journey
The chemicals industry is crucial to decarbonisation because it’s a major supplier of products to other industries. Many are very high profile - such as automotive, construction, food, and personal-care – so scrutiny will be high. It’s why two-thirds of Europe’s largest chemical end users in Europe are committed to reducing greenhouse-gas emissions by 2030, and over a third have pledged net-zero targets by 2050. But although chemicals industry … [Read more...]
China didn’t sign the global pledge to triple Renewables and double Efficiency. Why?
Announced at COP28, a total of 123 countries committed to tripling renewable power capacity and doubling energy efficiency by 2030. China didn’t. Why? Quoting experts, Lin Zi at China Dialogue explains that the bundling together of the two targets is the problem. Tripling renewables is very achievable; in fact China may well exceed that target. But reducing energy intensity is not easy, even though China has a good record: among the G20 members, … [Read more...]
Five major outcomes from COP28 (and next year’s is in Azerbaijan, another oil and gas producer)
Mark Maslin, Priti Parikh and Simon Chin-Yee at UCL lay out the five major outcomes from the latest COP28 climate summit in the UAE, a major oil and gas producer. Though in the run up there was great hope for a new climate agreement on the phasing out of all fossil fuels, that never happened. Phase out turned into a “transition away from.” The authors note that the first ever mention of fossil fuels in an international climate agreement was only … [Read more...]
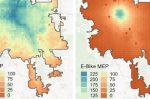
How practical is an E-bike compared to a Car: time, cost, energy
As e-bikes proliferate in cities around the world, there is a growing need to measure how practical an e-bike is compared to a car, and why. Julia Thomas at NREL describes research there that evaluates usefulness using the Mobility Energy Productivity (MEP) metric. The MEP quantifies the ability of an area's transportation infrastructure — given any specific travel mode — to connect individuals to goods, services, employment opportunities, and … [Read more...]
Improved “Solar Thermochemical” process captures 40% of the sun’s heat to produce Green Hydrogen
The U.S. Department of Energy has set a goal to make green hydrogen domestically at $1 per kilogram by 2030. Current costs range from $3 to $8 and none of it is being done at scale. Getting the cost of green hydrogen down is a serious concern for policymakers and industry alike. Most efforts are through electrolysis, which used electricity to split the water that delivers the hydrogen production. Jennifer Chu at MIT describes research there on … [Read more...]
What does cutting-edge Smart Metering look like as Grids become increasingly complex?
The global growth in electrification means grids everywhere are facing new opportunities as well as big challenges. Intermittent renewables, distributed energy generation, and the need to use every kWh as efficiently as possible means Distribution System Operators (DSO), in particular, must deploy optimisation solutions, and fast. Gridspertise provides state-of-the-art solutions for the digital transformation of electricity distribution networks. … [Read more...]
Will AI queries increase Data Centre energy use by an order of magnitude?
Data centres globally consumed 220-330 TWh in 2021 (California uses around 278 TWh/year). How much more will they consume if AI takes off, given AI queries consume an order of magnitude more energy, and there are over 5bn internet users worldwide? The first step is to make a decent evidence-based prediction, but the U.S. and the EU are only expected to enforce reporting requirements next year, explains Meredith Fowlie at UC Berkeley’s Energy … [Read more...]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 9
- Next Page »