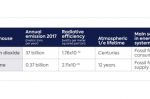
Robert Kleinberg at CGEP explains why methane isn’t included in the EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) which imposes a carbon tax on imported goods. Basically, CO2 emissions are easy to estimate accurately, whereas methane emissions are not. Many methane emissions, even the largest ones, are intermittent and of highly variable duration. Gas leaks vary over many orders of magnitude, and once diffused in the atmosphere leave no local … [Read more...]
Carmakers must stop complaining and meet the 2025 EU CO2 target (like they did in 2020, and profitably)
In 2025, the EU’s car CO2 regulation will require a 15% reduction of fleet emissions from new passenger cars sold in Europe, compared to 2021 figures. But some carmakers are saying this target is unfair, claiming that they cannot control the consumers’ appetite for EVs. They want targets relaxed or fines waived. Julia Poliscanova at T&E explains why their complaints are unwarranted for a number of reasons. Previous deadline dates show that EV … [Read more...]
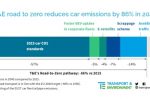
Roadmap to reduce EU car fleet emissions 86% by 2040
T&E has just published its car decarbonisation roadmap. It shows that the EU’s car CO2 standards, including the phase-out of combustion car sales in 2035, is the single most important emission reduction measure. But if the EU is to hit its newly proposed 2040 climate target - a 90% CO₂ reduction across the European economy by 2040 - it will need to deal with a significant amount of ICE (internal combustion engine) cars already on the road. … [Read more...]
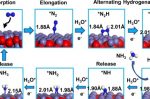
Research into how electrons and protons couple at an electrode can create more efficient fuel cells, electrolysers
Every efficiency gain discovered in the lab feeds through to the final cost of electricity. Anne Trafton at MIT describes new research looking at how electrons and protons couple at an electrode surface, which drives electric current. It’s a critical step in many energy technologies, including fuel cells, hydrogen electrolysers, batteries, and CO2 conversion into chemical fuels. The first step was to develop a way to design electrode surfaces … [Read more...]
The link between global GDP growth and CO2 emissions is weakening rapidly. Will emissions peak well before 2030?
Economic growth has been closely tied to rising greenhouse gas emissions since the industrial age. But data now clearly shows that that GDP growth and CO2 emissions are diverging. Siddharth Singh at the IEA presents the numbers. In advanced economies that divergence now seems locked in, with 2007 marking the moment of peak emissions (and not simply because of offshoring manufacturing). Even in developing economies GDP growth is far outpacing … [Read more...]
EU ETS or national climate targets? We need both
The choice between using the EU ETS or national climate targets to decarbonise is a false dilemma. We need both, explains Chiara Corradi at T&E writing for the Florence School of Regulation. There are plenty of examples where a carbon market and national targets have delivered good results together, as in Germany, Finland, Denmark and Portugal. And, looking ahead over the next few decades, the right policies should be able to cope with ETS … [Read more...]
16 innovative firms driving Aviation’s transition to net-zero
The Sustainable Aviation Challenge has identified 16 innovative firms that can accelerate the development and adoption of sustainable aviation fuel and other propulsion solutions. Aviation accounts for 2% of global emissions and, so long as lightweight compact clean aviation fuels are unavailable, this number is likely to increase along with air travel projections. Gianluca Gygax at the World Economic Forum lists the 16 firms, who will now be … [Read more...]
Making solid fuel from captured CO2 (with a 96% conversion rate)
What if CO2 could be captured and, rather than locked away underground for eternity, turned into a stable powder that can be used in fuel cells to produce electricity? David Chandler at MIT describes research there and at Harvard that has demonstrated a new process that has a 96% conversion rate. It’s been tried before, but the conversion rates were an unusable 20%. The CO2 is converted into formate and used like hydrogen or methanol (both strong … [Read more...]
Why we need a European Central Carbon Bank within the EU ETS framework
The EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) is at a critical juncture as it navigates a path towards achieving a net-zero Europe by 2050. Amidst this transformation, the proposal to create the European Central Carbon Bank (ECCB) has sparked a range of criticisms. Some critics have raised valid concerns about the feasibility, necessity, governance, and potential drawbacks of such an institution. Robert Jeszke and Sebastian Lizak at the Centre for … [Read more...]
Electrochemical Carbon Capture: a cheaper one-step process, power by clean energy
Carbon capture is expensive. Hence continuous attempts in laboratories around the world to find new ways to capture CO2 that are simpler and cheaper. One problem with the traditional method is that it is a two-step process, and energy intensive (therefore powered by high-heat fossil fuels). Jennifer Chu at MIT describes a new electrochemical method that separates out CO2 in a single step, and it’s powered by clean energy. It’s particularly … [Read more...]
Carbon Capture: how all Germany’s captured CO2 can be used by the Chemical industry
The German government is promising to publish a strategy on carbon capture, opening a door that has previously been closed to developing this technology. In the first of a series of articles, Simon Göss and Hendrik Schuldt at carboneer look at why the nation is changing its mind, before laying out the reasons why carbon capture will be essential for Germany to meet its emissions goals. Unlike the power grid, there’s no easy way to decarbonise … [Read more...]
Norway’s Sleipner and Snøhvit CCS: problems expose limitations of the science, regulations and multi-decade commitment
The offshore carbon capture and storage (CCS) projects of Norway’s Sleipner and Snøhvit are often cited as good case studies for the viability of the technology. Other CCS hubs are being proposed from Malaysia to the North Sea to the Gulf of Mexico, larger by factors of 10 or more. But how viable are they? Grant Hauber at IEEFA summarises his in-depth report on the risks. Both Sleipner and Snøhvit, operating since 1996 and 2008 respectively, have … [Read more...]
Carbon Capture rates of 60% sound impressive. But rising carbon prices could still make you commercially unviable
Mainstream scenarios state the unavoidable need for continued use of fossils through to 2050. For the world to stay within its carbon budget, that means the unavoidable need for carbon capture and plugging “fugitive” leaks. Chris Bataille at the Center on Global Energy Policy flags up the danger that new CCS projects with seemingly impressive capture rates of up to 60% may nevertheless become commercially unviable as carbon prices rise: that … [Read more...]
Farming Algae for Carbon Capture: new research cuts “fouling.” Scale-up in 3 years?
Natural marine algae already account for 50% of global CO2 removal. Farming it at scale in artificial tanks or tubes would take up a fraction of the land footprint of terrestrial plants. And algae can grow up to 50 times more quickly than land-based plants. It could be a game-changer that brings carbon capture costs down and make it a commercial reality. Here, David Chandler at MIT explains how new research there can make farming algae much more … [Read more...]
Ammonia from water microdroplets: lab demonstrates cheap, low-tech production
Very early stage research has discovered a new way of making ammonia cheaply, on a small scale (or large, if you want!), and with no harmful emissions, explains Adam Hadhazy writing for Stanford University. The process uses a cocktail of water, nitrogen gas, and a solid catalyst sprayed through a simple, low-tech instrument to make the ammonia. In contrast, the existing industry-standard Haber-Bosch process is energy intensive, large scale, and … [Read more...]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 6
- Next Page »