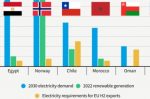
The EU’s RePowerEU plan, quickly made in response to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, aims to produce 20m tonnes of renewable hydrogen by 2030, with half coming from imports. Here, T&E summarise their report that concludes this is unrealistic. The report looks at six key countries with plans to export hydrogen to the EU: Norway, Chile, Egypt, Morocco, Namibia and Oman. T&E says these countries combined would only be able to deliver a quarter … [Read more...]
District Heating: Molten Salt boilers beat Water for storing intermittent Wind & Solar power
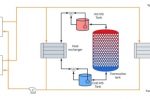
District heating networks, an important part of the energy transition for buildings, need a way of storing intermittent wind and solar power. But water tanks have limits: they take up a lot of space, and have a low thermal energy storage density (limited by the 100°C boiling point). Molten salts have a much higher storage density (regular table salt has a melting point of 801°C), but a melting point that is too high is not safe where ordinary … [Read more...]
Ammonia from water microdroplets: lab demonstrates cheap, low-tech production
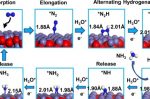
Very early stage research has discovered a new way of making ammonia cheaply, on a small scale (or large, if you want!), and with no harmful emissions, explains Adam Hadhazy writing for Stanford University. The process uses a cocktail of water, nitrogen gas, and a solid catalyst sprayed through a simple, low-tech instrument to make the ammonia. In contrast, the existing industry-standard Haber-Bosch process is energy intensive, large scale, and … [Read more...]
Can Enhanced Geothermal Systems be used as grid-scale batteries? Anywhere!
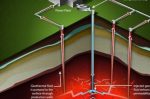
The US Department of Energy aims to cut the cost of Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) by 90% by 2035. Standard geothermal power comes from tapping existing hydrothermal reservoirs. But most places don’t have hot water reservoirs underground. EGS pumps water down to reach hot rocks, heating the water to achieve the same purpose. Everywhere has hot rocks underground. Here, Stefan Ellerbeck, writing for the World Economic Forum, describes research … [Read more...]
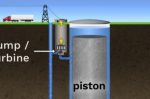
Gravity Batteries: any nation can do it at scale using rocks
The beauty of gravity batteries is that they simply involve lifting (charging) and lowering (discharging) a heavy weight, explains Simon Read writing for the World Economic Forum. For pumped hydro, access to water and a geological height difference is needed. But if you’re using rocks or bricks, anyone can do it anywhere, and at any scale. The rest is just a construction job. No rare materials or minerals will ever be needed, nor chemicals that … [Read more...]
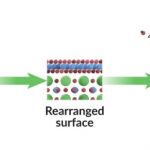
New research into making water boil using less energy
Can the boiling of water be done more efficiently? If so, a wide range of processes can save energy, not least the standard use of steam turbines in electricity generators. David Chandler at MIT describes research there that modifies the surface of the heating element. A combination of microscale dents and nanoscale bumps and ridges on the surface, and pillars that allow the “wicking” of water by capillary action, improves the efficiency of … [Read more...]
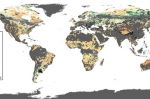
Global map of the future cost of clean Hydrogen production in 2030 and 2050
The world’s commitment to hydrogen needs an assessment of which regions can make it the cheapest. Herib Blanco at IRENA and Jacopo de Maigret at Fondazione Bruno Kessler describe their study of the range of factors that affect the future cost and therefore the potential for clean renewable hydrogen, estimated for 2030 and 2050. The main drivers are the capital cost of the renewable generation and the electrolyser, the cost of capital, and the … [Read more...]
“Floato-voltaics”: floating solar farms on existing municipal water reservoirs
The municipality of Cohoes, population 17,000, in New York State, is building a floating solar farm on its 10-acre water reservoir. It should power all the city-owned buildings and streetlights, save $500,000/year in electricity costs and still leave 40% of the generated electricity remaining for other civic use. It will cost $6m. It will be a first for a U.S. city, explains Connor O'Neil at NREL. The case for city “floato-voltaics” is so … [Read more...]
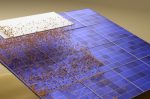
Using electrostatic repulsion to clean Solar panels, avoiding up to 30% power loss
Dust build-up on solar panels can reduce the power output by as much as 30% in just one month. Even a 1% reduction in power for a 150MW solar installation could result in a $200,000 (€180,000) loss in annual revenue. Cleaning normally requires purified water, but that needs to be trucked in to prime locations like deserts where solar potential is highest. Cleaning with brushes is labour intensive and can damage surfaces irreparably. David … [Read more...]
Hydrogen production in 2050: how much water will 74EJ need?
There’s no point ramping up hydrogen if other resource constraints are going to bring it to a halt. Here, Herib Blanco at IRENA summarises their research into how much water will be needed in the production of hydrogen through electrolysis (i.e. from water) and the costs involved. A wide range of analyses have been reviewed to calculate the amount of water used during the hydrogen production, and by the energy source used to power it (renewables … [Read more...]
New research into Catalysts can boost Hydrogen manufacture
Catalysts are materials used to enable and accelerate a chemical reaction. There is a long history of using them in industry to manufacture different hydrocarbons, ammonia, sulfuric acid, and the list goes on. By choosing your materials well and tinkering with the structure at the molecular level, the catalyst can greatly improve the efficiency of the conversion process. Glennda Chui at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory describes how their … [Read more...]
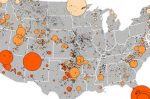
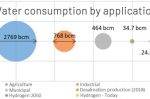
Energy sector is one of the largest consumers of water in a drought-threatened world
The implications of the global water footprint of energy generation are phenomenal, writes Gary Bilotta of the University of Brighton. He warns that if policy makers fail to take into account the links between energy and water, we may come to a point in many parts of the world where it is water availability that is the main determinant of the energy sources available for use. Courtesy The Conversation. … [Read more...]