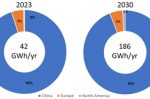
The recycling of lithium-ion batteries is vitally important to the future of electric power, explains Gregg Smith at Orbia Advance, writing for WEF. Making a battery has a significant carbon footprint of its own. Yet recycling can be one tenth the cost of manufacturing a battery from scratch. And energy security is enhanced by lessening dependence on mining countries and other suppliers. It’s why Europe will require new batteries to contain at … [Read more...]
A global review of Battery Storage: the fastest growing clean energy technology today
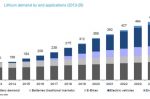
The IEA report “Batteries and Secure Energy Transitions” looks at the impressive global progress, future projections, and risks for batteries across all applications. 2023 saw deployment in the power sector more than double. Strong growth occurred for utility-scale batteries, behind-the-meter, mini-grids, solar home systems, and EVs. Lithium-ion batteries dominate overwhelmingly due to continued cost reductions and performance improvements. And … [Read more...]
Batteries made of super-hot sand: for long-duration grid storage at $4 to $10 per kWh
Our electric future needs low-cost long-duration storage for grids. Per kWh, pumped hydropower is about $60, compressed air energy storage (CAES) costs from $150 to $300, and lithium-ion batteries cost around $300 (and only store energy from one to four hours). Wayne Hicks at NREL describes research into thermal energy storage (TES) using solid particles such as sand which is abundant worldwide. With a duration lasting hundreds of hours, … [Read more...]
Iron-air batteries: long-duration grid storage targets 1/10th the cost of lithium-ion
Wind and solar need cheap, long-duration storage to even out its inherent weather-determined intermittency. Deborah Halber, writing for MIT News, describes the development of iron-air batteries. Iron is cheap and available worldwide. Storage duration is multi-day. They are much heavier and take up more space than lithium-ion batteries, but that doesn’t matter for immobile grid storage. The target price tag of $20/kWh (one-tenth the cost of … [Read more...]
China’s CATL to cut its EV battery costs by up to 50% this year, heralding a price war
China’s CATL, the world’s largest producer of EV batteries, is saying it will slash the cost of its batteries by up to 50% this year as part of a price war with China’s second largest maker, BYD subsidiary FinDreams. The main cause is the overproduction of batteries in China: the oversupply means prices must fall. Muhammad Rizwan Azhar, Waqas Uzair and Yasir Arafat at Edith Cowan University look at the causes and implications, but add that … [Read more...]
Organic cathode can replace Cobalt in Batteries: similar performance, faster charging, cheaper to make
In most lithium-ion batteries, the cathode contains cobalt. But cobalt is a scarce metal, found mostly in politically unstable countries, its extraction is hazardous for miners and generates toxic waste. And as demand for batteries globally keeps rising, so too will the cost of cobalt. Anne Trafton at MIT describes the development of an alternative cathode made of organic materials. Its structure is similar to graphite. It can conduct electricity … [Read more...]
Batteries are still getting exponentially cheaper, more efficient: ready to displace half of global fossil fuel demand by 2045?
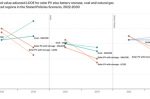
A new report by RMI says batteries are on the path to replace 175 EJ of fossil fuel demand in the power sector, 86 EJ of fossil fuels from road transport and can put at risk another 23 EJ from shipping and aviation. That equates to a phaseout of half of global fossil fuel demand in the next two decades. Daan Walter, Sam Butler-Sloss and Kingsmill Bond at RMI summarise the findings in six graphs with explanations. Battery sales are growing … [Read more...]
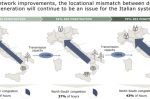
Italy: Capacity Auctions for 71 GWh of additional Grid Storage
Italy needs 71 GWh of new utility-scale electricity storage capacity by 2030 to meet EU targets to cut emissions by at least 55% by 2030, according to Terna which manages Italy’s transmission grid. ***STOP PRESS*** This Tuesday at 11:00 CET, Energy Post is exclusive media partner to a dedicated webinar (organised by ATA Insights/RENMAD) on Capacity Market Auctions REGISTER FREE HERE. In this article, Sara Stefanini summarises the Terna study, … [Read more...]
China is still playing the long game with its ‘new three’: solar cells, lithium batteries, EVs
China’s “new three” – or xin san yang – are solar cells, lithium-ion batteries, and EVs. The term harks back to the concept of its “old three” that were once the pillars of its exports: clothing, home appliances and furniture. China’s success is seen in the numbers: it accounts globally for 80%+ of solar cell exports, 50%+ of lithium-ion batteries and 20%+ of EVs. You Xiaoying, writing for China Dialogue, interviews experts and quotes reports … [Read more...]
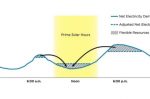
Modelling revenue potential for Germany’s Battery Storage future
In the last ten years Germany has installed battery storage systems totalling 6.5 GW of power and 10.1 GWh of energy. Storage is an essential part of every nation’s electrification plans: for peak shaving, uninterruptible power for industrial customers, use as a buffer, and self-supply in households. Elena Dahlem and Alex Schmitt at Energy Brainpool start with a summary of storage’s use in the household, industrial and large-scale sectors. They … [Read more...]
Make EV batteries bidirectional, get GWs of storage for the Grid
How to cope with the hourly, daily and seasonal variation in demand as regions electrify more, depend more on variable renewables like wind and solar, and cut baseload fossil generation? Storage shifts load nicely. But why build grid-scale batteries when millions of little batteries in our EVs are sitting idle in our driveways for most of the time? As Mark Specht at the Union of Concerned Scientists explains, it’s why in California a bill is … [Read more...]
Scaling up global grid-scale Storage to 80GW/year (it was 16GW in 2022)
Globally, annual additions of grid-scale battery storage must rise to 80GW between now and 2030, explain Amit Jain, Gabriela Elizondo Azuela and Aakarshan Vaid at the World Bank, writing for WEF. In 2022 it was only 16GW. The biggest gap, perhaps understandably, is in developing countries. It’s in these regions where renewables auctions for deployment – primarily solar and wind – need to start including hybrid storage as part of the package. The … [Read more...]
Concrete supercapacitor: works like a battery, much cheaper, easy to make
Capacitors work like batteries. They store and discharge electricity. David Chandler at MIT explains how researchers there have designed a supercapacitor from concrete and carbon black, two cheap and common materials. The beauty of the idea is that they can be incorporated into building foundations, thus installing a battery virtually for free. A concrete capacitor cube 3.5m wide can store 10kwh, enough for a household. Similarly, concrete … [Read more...]
Sodium-ion batteries ready for commercialisation: for grids, homes, even compact EVs
Sodium-ion (Na-ion) batteries, a much more abundant and cheaper alternative to the standard Lithium-ion, are on the verge of commercialisation, explain Carlos Ruiz, Martina Lyons, Isaac Elizondo Garcia and Zhaoyu Wu at IRENA. Though there’s enough Lithium in the world to support global electrification targets, tightening demand and supply chain constraints point at the urgent need for an alternative. The cost of a Na-ion battery cell is expected … [Read more...]
Circular Battery Economy: what policies and processes can accelerate recycling and reuse?
As battery production scales up so do the risks of the long global supply chain failing, or causing more emissions, damaging the environment, and breaching human rights. A circular battery economy should greatly reduce those risks. Yet the U.S. has no federal recycling mandates or requirements for lithium-ion batteries, and state policies are inconsistent. Marie McNamara at RMI maps out the five critical issues that must be dealt with. Before … [Read more...]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 5
- Next Page »