How do you double or triple your existing power transmission capacity when costs are rising and you face local opposition to the disruption? Zach Winn at MIT describes a new innovation that uses superconductors designed to transport five to 10 times the amount of power of conventional transmission lines, using essentially the same footprint and voltage level, carried on otherwise standard overhead lines. The superconducting cables (with much of … [Read more...]
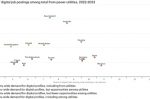
Digitalisation of the Energy sector: are Utilities hiring the skilled workers they now need?
Like many other sectors, the energy sector needs employees with digital skills. They need to create the new tools that can match power supply with demand, predict and detect faults in networks, and give greater control to consumers. It’s an essential part of the new world of decarbonisation, with digitalisation enabling the faster integration of renewables, improving grid stability and unlocking greater energy savings. Aloys Nghiem, Marc … [Read more...]
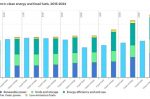
At $2tn, investment in Clean Energy in 2024 is set to be double that for Fossil Fuels
A new report by the IEA reveals that global spending on clean energy technologies and infrastructure is on track to hit $2tn in 2024, driven largely by attractive cost reductions, improving supply chains, energy security, and government policies. This is despite higher financing costs for new projects. The combined investment in renewable power and grids only recently overtook the amount spent on fossil fuels, in 2023. 2024 will see it at double … [Read more...]
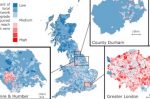
Upgrade the grid, or avoid by incentivising flexibility? Electricity demand mapping can tell you what to do
Power grids across the world need upgrading to accommodate the rapidly rising amount of electricity being generated. Without it, it is a serious bottleneck to the transition to clean fuels. Sheridan Few at the University of Leeds summarises his co-authored study that creates a map of where upgrades are most needed in the UK. The map’s purpose is twofold. Firstly, it predicts where power consumption will rise the most and the upgrades are … [Read more...]
How to handle rapid Grid load growth: Data Centres can set the template for EVs, Buildings, new Industry
Due to their growing power demand, data centres can set a precedent for how to handle rapid load growth in a way that supports the grid and ensures reliable, resilient, carbon-free electricity. In other words, they can set the template for the coming surges in demand from EVs, buildings electrification, and the new rich-world policies of onshoring industry and manufacturing, explain Alexandra Gorin, Roberto Zanchi and Mark Dyson at RMI. Big, … [Read more...]
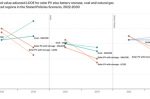
A global review of Battery Storage: the fastest growing clean energy technology today
The IEA report “Batteries and Secure Energy Transitions” looks at the impressive global progress, future projections, and risks for batteries across all applications. 2023 saw deployment in the power sector more than double. Strong growth occurred for utility-scale batteries, behind-the-meter, mini-grids, solar home systems, and EVs. Lithium-ion batteries dominate overwhelmingly due to continued cost reductions and performance improvements. And … [Read more...]
After the EU elections: what should be Europe’s energy and climate priorities for 2024-29?
After June’s European Parliament elections the new Commission will be tasked with setting the agenda for EU energy and climate policy. What should its priorities be? Maciej Jakubik at Forum Energii summarises their paper that sets out six. Energy security, improving access to data and therefore planning, energy market reforms and grid development, protecting and supporting vulnerable citizens, establishing an Energy Transformation Fund, global … [Read more...]
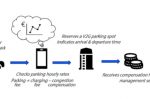
V2G: modelling how EV batteries can provide storage to the grid
V2G (vehicle-to-grid) technology allows parked EVs to store and/or inject electricity into the grid when needed. The main benefit is to avoid the expense and disruption of building dedicated large-scale grid batteries when EVs and charging infrastructure are already ramping up. Though most EVs and charge points are not V2G-ready, now is the time to plan ahead, measure the true potential and identify the challenges. Ibtihal Abdelmotteleb, Matteo … [Read more...]
What China, Germany, and Texas tell us about Capacity Adequacy
As intermittent renewables penetrate further into the grid mix, reliable firm power generation is needed for whenever there is a shortfall. But back-up power, by its nature, has unreliable utilisation rates. And up-front costs for new plants are high, be they gas-fired plants, coal, nuclear, or large-scale storage. That makes future profitability uncertain, and private investors nervous. Hence the need for “capacity mechanisms” that guarantee … [Read more...]
10% of global GDP growth came from the new Clean Energy economy in 2023
The clean energy economy is making its mark on global GDP, explain Laura Cozzi, Timur Gül, Thomas Spencer and Peter Levi at the IEA. It accounted for 10% of global GDP growth in 2023, primarily through three activities: manufacturing of clean energy technologies, deployment of clean power capacity, and clean equipment sales. Here, the authors present the in-depth results for four of the largest economies: the U.S, the EU, China and India, which … [Read more...]
Strict rules stop Green Hydrogen production diverting clean power from the grid. What are they?
Green hydrogen must be made from green electricity. But the electricity used for making it must fulfil stricter requirements than conventional green electricity. Matthis Brinkhaus at Energy Brainpool describes the criteria by which hydrogen can be designated as 100% renewable: Additionality; Additionality Plus; Temporal correlation, simultaneity; Geographical correlation, regionality. Brinkhaus points at where exceptions can be made, and where … [Read more...]
Batteries made of super-hot sand: for long-duration grid storage at $4 to $10 per kWh
Our electric future needs low-cost long-duration storage for grids. Per kWh, pumped hydropower is about $60, compressed air energy storage (CAES) costs from $150 to $300, and lithium-ion batteries cost around $300 (and only store energy from one to four hours). Wayne Hicks at NREL describes research into thermal energy storage (TES) using solid particles such as sand which is abundant worldwide. With a duration lasting hundreds of hours, … [Read more...]
Iron-air batteries: long-duration grid storage targets 1/10th the cost of lithium-ion
Wind and solar need cheap, long-duration storage to even out its inherent weather-determined intermittency. Deborah Halber, writing for MIT News, describes the development of iron-air batteries. Iron is cheap and available worldwide. Storage duration is multi-day. They are much heavier and take up more space than lithium-ion batteries, but that doesn’t matter for immobile grid storage. The target price tag of $20/kWh (one-tenth the cost of … [Read more...]
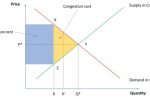
Europe’s cross-border Interconnectors: how JAO auctions optimise energy flows, prices
Interconnectors allow for cross-border flows of energy between two markets that would otherwise not be connected. Through an economic convergence between supply and demand, the cheapest marginal producer located anywhere in these two markets should be able to set market prices. As Jean-Baptiste Vaujour at the Emlyon Business School explains, the central question is to find an optimal allocation of the scarce interconnection capacity between the … [Read more...]
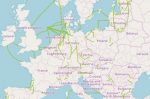
Financing Europe’s cross-border Interconnectors to deliver energy security, lower prices: a look at incentives and policies
The EU and its Member States are building out interconnectors to improve security of supply and affordability of electricity through the physical and economic linking of national energy markets into a single, synchronised European market. But each interconnector is expensive, complex and therefore risky. They can span long distances or natural obstacles such as mountains or seas. Significant network planning and adaptation is needed to account … [Read more...]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 12
- Next Page »