As the Paris Olympics begins, Mark Charlton at De Montfort University tells us how sport is being affected by climate change. Rising temperatures and weather events like flooding and droughts are impacting sports including athletics, football, cricket, golf, skiing and more. And it’s not just about the direct effect on the athletes. Kit design is moving away from pure streamlining to creating garments that wick sweat away and keep body heat down. … [Read more...]
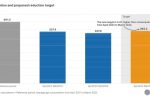
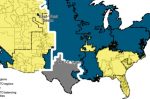
REPowerEU gas reduction is exceeding targets. But that means the same 2025 target can see gas rise again
The REPowerEU policy has done well so far in its aim of ending Europe’s dependency on Russian fossil fuels by 2027. The target of 15% reduction in gas use, compared to the average consumption between April 2017 and March 2022, was exceeded in both 2023 and 2024. The Commission has again set the same 15% target for the coming year. However, by doing so the very many EU countries that have succeeded so well in exceeding that target are effectively … [Read more...]
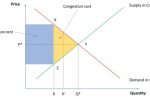
Europe’s cross-border Interconnectors: how JAO auctions optimise energy flows, prices
Interconnectors allow for cross-border flows of energy between two markets that would otherwise not be connected. Through an economic convergence between supply and demand, the cheapest marginal producer located anywhere in these two markets should be able to set market prices. As Jean-Baptiste Vaujour at the Emlyon Business School explains, the central question is to find an optimal allocation of the scarce interconnection capacity between the … [Read more...]
EU’s fossil fuel CO2 emissions drop to levels last seen in the 1960s
The EU’s CO2 emissions from fossil fuels (including power generation, industry and transport) dropped 8% in 2023 year-on-year, reaching levels last seen in the early 1960s, reveals an analysis by CREA. More than half of that decline came from an impressive 25% year-on-year reduction in CO2 emissions from power generation. The cleaner electricity mix is thanks to the continuous rise of wind and solar as well as a rebound in hydropower and nuclear. … [Read more...]
How to manage price risk as the EU shifts from Russian Gas to Renewables
Europe is phasing out Russian gas and replacing it with more renewables. That means there will be greater demand variability and a resulting impact on European spot gas prices. The problem is that long-term contracting, the traditional way for buyers to mitigate spot price risk, is incompatible with Europe’s climate objectives of reducing long term consumption of gas. Kong Chyong at the Center on Global Energy Policy proposes alternative policy … [Read more...]
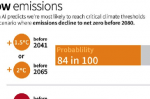
New AI model predicts 1.5C temperature rise is likely in 2030s even if emissions decline
A new artificial intelligence model is predicting that 2C warming is likely to occur and sooner than expected, even if current low-emissions strategies are successful, explains Josie Garthwaite at Stanford University. The Stanford-developed AI uses “neural network” learning from vast quantities of past data, predicting that the 1.5C threshold is likely to be crossed in the next 10 to 15 years. That’s regardless of how much greenhouse gas … [Read more...]
The U.S. needs a plan to transfer electricity long distance between regions, like Europe and China
In the U.S. several hundred thousand miles of power lines connect thousands of electric generators. But whereas Europe and China, at a similar scale, have continental-scale grid development plans, the U.S. does not. Its grid is highly fragmented and consists of not one, but three separate power grids that are almost completely isolated from one another. It has twelve different transmission planning regions that must coordinate much better to cope … [Read more...]
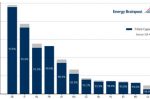
European gas prices have fallen sharply since August. What happens next?
Prices on the European gas market have fallen sharply since August 2022 and Europe’s gas storage facilities are almost full. That’s good news, but the problems aren’t over. Simon Göss at cr.hub, writing for Energy Brainpool, explains why by looking at the data. He runs through the main factors driving the changes, primarily strong LNG imports, Norway’s increased production, mild weather, and lower gas consumption (particularly in industry). … [Read more...]
Electricity market re-design should focus on the root cause of the crisis, Europe’s dependence on fossil fuels
Amidst the perfect storm of the pandemic, war in Ukraine, and extreme weather events, Bruce Douglas at Eurelectric urges us all not to lose focus on our decarbonisation targets. Energy savings, electrification and renewables are more important than ever to help reduce dependence on fossil fuels. Douglas explains that Europe’s electricity sector remains totally committed to the drive towards clean energy, citing examples. He summarises the … [Read more...]
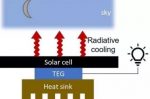
Next-gen Solar farms that work at night, in the rain, and self-clean
With the worldwide roll-out of solar, raising the efficiency of energy conversion isn’t just about the materials science of PV cells. Douglas Broom, writing for the World Economic Forum, runs through three “add-on” innovations. Researchers have found a way to generate electricity in the dark as panels cool during the night. A low-cost thermoelectric generator works using the temperature difference between the cooling solar panels and the … [Read more...]
Imagine it’s 2030 and net-zero is on track. How did we do it?
Imagine it’s 2030. The energy transition is on track and net-zero goals are entrenched across the global economy. How did we get there? Tim Buckley at IEEFA imagines it for us and sends us a postcard from the future. Writing in the past tense, he flags actual events and policies happening today to “remember” the major changes that took place to achieve it. Weather-related disasters compelled governments to act, recognising – apart from the … [Read more...]
IEA WEO 2021 message to COP26: 40% of clean energy goals will cut costs
The IEA’s latest World Energy Outlook was published on Wednesday. This year’s WEO-2021 is released earlier than usual to inform COP26 and, for the first time, is available for free to ensure the widest possible audience. Simon Evans at Carbon Brief offers his summary of the 386-page report, quoting relevant numbers and charts. He first points to the new scenario, Net-Zero Emissions by 2050 (NZE), as the IEA’s recognition that this is what … [Read more...]
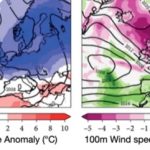
Optimising Wind and Solar needs new ways of weather forecasting
Weather forecasters are used to – and very good at – predicting large-scale weather patterns and then inferring what the actual surface weather conditions will be, based on a database of past events. Hannah Bloomfield at the University of Reading explains how the creation of a database of site-specific wind and solar generation, as well as grid demand, can be used in the same way to more accurately predict the impact of the weather on these … [Read more...]
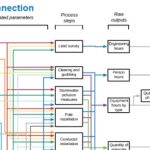
Modelling total costs for Onshore Wind power plants: from site prep to grid connection
The costs of wind turbines is dropping. But that means all the other capital costs - site preparation, foundations, infrastructure, tower construction – will become a bigger part of the total. In the U.S. they currently account for around 30% of the capital expenditures needed to install a land-based wind plant. To keep those costs under control the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) has created a comprehensive open-source modelling … [Read more...]
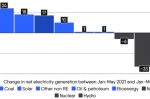
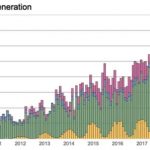
Britain has shifted 30% of its electricity away from fossil fuels in just nine years
Britain’s extraordinary energy transition is in part down to increased energy efficiency: put simply, less electricity was needed, whatever the source. But coal is still essential during spikes in demand. Given coal generation is due to be phased out by 2025, the country will need to find alternative power sources to cope during extreme weather events. And that overall decline in electricity demand is sure to be reversed as more vehicles and … [Read more...]