How can we lower the lifetime emissions of building materials? Bernardino D'Amico at Edinburgh Napier University references his research to show how hemp-based materials can substitute for concrete. And it’s even more effective than timber, a popular low-carbon alternative. Growing industrial hemp can absorb twice as much CO₂ compared to growing trees. Raw hemp fibre can be processed into panels and mats for thermal or acoustic insulation. Hemp … [Read more...]
EU ETS2 for Buildings, Road Transport in 2027: why we need auctions to start early
The EU has established a second emissions trading system (ETS) to put a carbon price on buildings and road transport, the “EU ETS2”. The ETS2 starts in 2027, but monitoring and reporting of ETS2 emissions will begin in 2025. One issue is that an ETS means prices for long-term fuel supply contracts will be affected, so a crucial question for firms is how to hedge their potential exposure, says Ingo Ramming at BBVA writing for the Florence School … [Read more...]
Infrared Fabric heat-emitting “wallpaper” avoids the disruption and expense of Heat Pumps
Hundreds of millions of buildings across the world need clean heating. But retrofitting them all for heat pump installation is going to be expensive, disruptive, and take a long time. Michael Siebert at Nottingham Trent University describes a completely different approach, using new high-tech infrared fabrics that emit heat. Made of graphene, they can be installed as easily as wallpaper. The radiated heat can be felt instantly, unlike the slow … [Read more...]
Buildings: how can Europe reduce emissions from Construction?
11% of global energy-related carbon emissions are embedded in the construction of buildings. Though focus has been on reducing operational emissions (28%, from heating and cooling, power etc.) there is not enough attention paid to construction, explains Carolina Kyllmann at CLEW. She looks at all the issues, including production of materials, transport to the site, construction, renovations, demolition and reuse of materials, and more. Kyllmann … [Read more...]
District Heating: Molten Salt boilers beat Water for storing intermittent Wind & Solar power
District heating networks, an important part of the energy transition for buildings, need a way of storing intermittent wind and solar power. But water tanks have limits: they take up a lot of space, and have a low thermal energy storage density (limited by the 100°C boiling point). Molten salts have a much higher storage density (regular table salt has a melting point of 801°C), but a melting point that is too high is not safe where ordinary … [Read more...]
2024 a tipping point for Sustainable Buildings? Demand now outstrips supply in major cities
Guy Grainger at JLL, writing for WEF, believes 2024 will be the tipping point when returns for investing in sustainable office buildings will start to pay dividends for building owners. That’s because, according to JLL research, there is now a good premium on rents for sustainable buildings in important locations: just over 7% across eight cities in North America, around 10% across nine cities in the Asia Pacific and more than 11% in London. In … [Read more...]
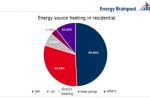
Heat Pump + Gas Boiler hybrids can reduce bills and emissions faster than a 100% heat pump roll out
The reduction in buildings emissions is well off track, not least in the residential sector. Something governments and millions of households are well aware of. The problem with replacing a gas boiler with a heat pump is the up-front cost and disruption. Installing the heat pump alone can cost several thousands more than replacing a gas boiler. On top of that, you should properly insulate your home and replace the radiators. Jovana Radulovic at … [Read more...]
Thermal Energy Storage for heating and cooling Buildings: finding materials that melt at room temperature
Thermal Energy Storage (TES) in individual buildings can cut heating and cooling costs while delivering grid stability, explains Ryan Horns writing for NREL. Back in the 1800s blocks of ice were shipped to cities to cool buildings down. Today, research is underway to identify materials that can be heated or cooled by excess grid power and release or absorb heat when needed. Similarly, materials are being researched and developed that “phase … [Read more...]
Germany to ramp up the decarbonisation of Buildings Heating from Jan 1st 2024. How?
Decarbonising heating is a major challenge for any country. Germany’s Building Energy Act (GEG) means that from 2024 every newly installed heating system, in new or existing buildings, must operate with a minimum of 65% renewable energy. Concerns over the costs to customers (installing new and expensive systems, or paying a penalty for fossil heating) has led to intense debates, hence the new law includes a range of subsidies, bonuses, discounted … [Read more...]
Building Materials “Embodied Carbon”: reaching net-zero with low-carbon cement, timber, modular design and more
In this explainer Madeline Weir, Audrey Rempher and Rebecca Esau at RMI first describe how embodied carbon is calculated. They then summarise the strategies being employed to reduce it, including using low-carbon, carbon-neutral, or even carbon-storing materials. New cement formulations are being developed with over 60% less CO2 emissions than the regular kind. Low-carbon mass timber is an alternative building material under development. On the … [Read more...]
Buildings Efficiency: cars have an “eco mode” button. Why not our homes?
Households need the right tools to be able to take control of their real-time energy consumption, says Maximilian Auffhammer at the Energy Institute at Haas. Smart meters are just too crude. They don’t tell you how much energy individual devices are using – fridges, ovens, heaters, EV chargers, TVs, lightbulbs, toasters, etc. You have to work it out yourself by switching devices on and off and seeing the difference. Auffhammer argues if you price … [Read more...]
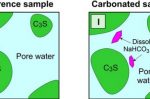
Adding ordinary baking soda to concrete production can cut 15% of its CO2 emissions
Concrete production makes up 8% of global CO2 emissions. Half comes from the fossil energy used to make it (which, hopefully, can transition to clean power), and the other half comes from the CO2 that escapes during the chemical transformation. David Chandler at MIT describes research there that shows how simply adding sodium bicarbonate (yes, the baking soda you put in your cookies) during the early stages of production can remove, by … [Read more...]
Buildings “Energy Performance Certificates”: piloting new tools to ramp up renovations
In Europe, any building put up for sale or rent must have an Energy Performance Certificate (EPC). But as climate ambitions rise, so too must the those of the EPC. That's the purpose of the TIMEPAC consortium, funded by the EU’s Horizon programme, is working to extend its effectiveness and range of tools, explains Patricia Contreras Tejada writing for the European Science Communication Institute (ESCI). She quotes experts who point out that a low … [Read more...]
Solar PV windows on highly glazed skyscrapers can cut energy by 40%+
Around a third of the world’s energy consumption and CO2 emissions come from buildings. Highly glazed skyscrapers and buildings may look beautiful and let in plenty of light, but waste a lot of energy due to the extra cooling needed in summer and heating in winter. Modern skyscrapers can have window-to-wall ratios of 70%+. But modern thermally efficient photovoltaic windows not only provide insulation but turn the absorbed light into power. Wayne … [Read more...]
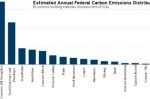
New U.S. ‘Buy Clean’ plan earmarks billions for low-carbon cement, steel and other building materials
New guidance from the U.S. federal government, combined with historic Inflation Reduction Act investments, could turbocharge markets for low-carbon cement, steel, and other building materials. Victor Olgyay, Anish Tilak and Connor Usry at Rocky Mountain Institute explain how the new “Buy Clean” recommendations will mean the procurement of green building materials for federal building and transportation projects. That will lead to a boost in … [Read more...]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 5
- Next Page »