Biofuel producers are always looking for low carbon intensity feedstocks. Corn stover (the waste from harvested corn) is typical, but harvesting is seasonal. Jeffrey Wolf at NREL explains how research has led to the development of XanoGrass. It is a perennial, so can be harvested all year round. It can be grown on marginal or even “unfarmable” lands, so existing food crops won’t be displaced. No special farming equipment is needed, so existing … [Read more...]
Germany, Italy + 10 others not on track to meet their 2030 climate targets, costing them €billions in carbon credits
12 EU countries are on track to miss their 2030 national climate targets by a large margin, according to a study by T&E. That means they will have to buy carbon credits on such a large scale there will be few left for others to buy their way out of missing their own targets (leaving them facing court cases). Germany and Italy are the two worst performing countries, with France on track by a very close margin. Germany will have to pay … [Read more...]
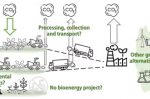
When can Bioenergy be truly green? 5 key questions for every project
Is bioenergy green? It depends, says Jessica Allen at the University of Newcastle. She lays out five key questions that should be asked about every bioenergy project. What is its source? Native forest residues, dedicated fast-growing biomass species, agricultural residues and “waste” biomass: all have pros and cons that must first be carefully measured. How many emissions are embodied in the collection and transport of the biomass to the plant? … [Read more...]
Biogas from dairy farms: what incentives can make it commercially viable?
Anaerobic digesters are used to turn cow manure into useable methane fuel. But the raw cost of that gas is ten times the market price. On the plus side, emissions are being avoided. So how do you create the incentives that are fair and make it commercially viable? In California, dairy biogas has risen from almost non-existence five years ago to delivering half of all natural gas used for transportation in the state. Aaron Smith at the Energy … [Read more...]
EU ETS or national climate targets? We need both
The choice between using the EU ETS or national climate targets to decarbonise is a false dilemma. We need both, explains Chiara Corradi at T&E writing for the Florence School of Regulation. There are plenty of examples where a carbon market and national targets have delivered good results together, as in Germany, Finland, Denmark and Portugal. And, looking ahead over the next few decades, the right policies should be able to cope with ETS … [Read more...]
EU Carbon Removal Certification Framework: new rules to turn greenwashing into genuine removals
The EU Carbon Removal Certification Framework intends to drive forward technological and natural carbon removals, and prevent greenwashing through robust standards and certification procedures. It’s to deal with the existing poorly monitored carbon removals market: the lack of oversight, transparency, trustworthiness, and genuine climate impact (additionality) of projects and certificates. Simon Göss at carboneer looks at the current proposals, … [Read more...]
Can Phytomining deliver Critical Minerals at scale: farming plants that accumulate high metal concentrations
Both Europe and the U.S. are making plans to secure supplies of critical minerals as the transition gains pace. Domestic mining or securing import deals with close allies is the main focus. Here, Maria Krol-Sinclair and Thomas Hale at CSIS review the prospects for a new method that will require neither: phytomining. Some plants, called hyperaccumulators, soak up high concentrations of metals into their leaves, bark, and roots. These plants can … [Read more...]
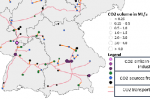
Germany is developing a strategy for Carbon Capture and Storage to meet its 2045 net zero target
Germany cannot become carbon neutral by 2045 without carbon capture, explains Simon Göss at carboneer. It’s why the German government is developing a Carbon Management Strategy for CO2 storage and utilisation. Projections reveal that around 30m tons of CO2 will have to be captured, transported, reused or disposed of by 2045. The focus will be on industrial processes and waste. Göss lays out the background to Germany’s strategy, including possible … [Read more...]
Turning waste biomass into clean fuel: cheap, portable equipment, cuts emissions, earns income for rural poor
The burning of biomass accounts for 10% of primary energy used worldwide: wood, peat, animal dung, corn stalks, rice husks, hay, straw, and other agricultural waste. Billions of people, mainly in remote and poorer regions, rely on such fuels for cooking, heating, and other household needs. But it’s a major source of emissions as well as pollution. And, annually, an estimated $120bn worth of crop and forest residues are burned out in the open … [Read more...]
New U.S. study: damage per ton of CO2 costs $185, not the official $51
Maximilian Auffhammer at the Energy Institute at Haas reviews a new paper that suggests CO2 causes over three times as much damage in dollar terms as the figure currently used by the US government, $51 per ton. The new study shows $185 per ton of CO2 as the Social Cost of Carbon (SCC). The updated model is superior to previous models, says Auffhammer. It’s also open source, so anyone can use it, criticise it, and tweak the numbers to get … [Read more...]
EVs vs Biofuels: new study looks at ethanol’s impact on agricultural land use, food prices, emissions
For transport, biofuels have lower emissions than gasoline/petrol, but EVs will have the lowest emissions of all. Hence the opposition to those biofuels, along with objections to the valuable cropland used to make the ethanol. But the overall advantage depends on the speed of transition to EVs charged with clean electricity. Now, a calculation has been made of the amount of agricultural land preserved for global food production - or kept as … [Read more...]
Methane emissions reach unexpected new highs. Is climate change causing a runaway effect?
Simon Redfern at Nanyang Technological University, Singapore summarises his co-authored study that says methane emissions are four times more sensitive to climate change than that estimated in the latest IPCC report, which was only published in February 2022. The study follows the observation that, despite the pandemic stalling the world economy, methane emissions have reached new highs. Not because methane emissions have risen but because … [Read more...]
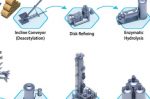
SAFFiRE: cheap, Sustainable Aviation Fuel from agricultural waste
SAFFiRE (Sustainable Aviation Fuel From [i] Renewable Ethanol) is a 10-ton-per-day pilot plant project. The goal is 7bn gallons of sustainable, low-carbon aviation fuel by 2040. Ryan Horns at NREL explains that the sustainable fuel is made from corn stover, an agricultural waste product, chemically broken down into sugars that can then be converted to fuels. The SAFFiRE process can take advantage of the existing infrastructure of over 200 ethanol … [Read more...]
All estimates of the ‘cost’ of climate action should include the savings and benefits
Too many climate mitigation scenarios calculate the cost of that transition without measuring the savings and benefits, explain Alexandre Köberle and Joeri Rogelj at Imperial College London, Toon Vandyck at the EC's Joint Research Centre, and Celine Guivarch at the Centre International de Recherche sur l’Environnement et le Developpement, writing for Carbon Brief. This leads to a pessimistic view of the challenges ahead, and public aversion to … [Read more...]
COP26: a strategy for tackling “imported deforestation”
Palm oil, beef, cocoa, coffee, soy, and other agricultural products are responsible for deforestation in the producing countries. Of the 10m hectares of tropical forest lost each year, two-thirds can be unambiguously attributed to agricultural expansion and international trade is responsible for about half of this. The EC is due in December to unveil a legislative proposal to address the issue. Alain Karsenty and Nicolas Picard, writing for IFRI, … [Read more...]