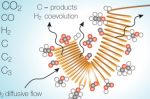
Producing sustainable e-fuels like ethanol and butanol requires the processing of biofeedstocks. Using microbes to chew their way through them is well known. Justin Rickard at NREL describes research there that has found a much more efficient way, using electron-bifurcating enzymes. Flavin-based bifurcating enzymes are biocatalysts that have evolved to perform efficient metabolic reactions in harsh environments with low nutrients. The researchers … [Read more...]
Turning Ethanol production’s CO2 by-product into E-Fuels using Wind power
With vast open spaces, Midwest states in the U.S. produce millions of gallons of ethanol from corn as well as thousands of kilowatt-hours of electricity from wind farms every year. Research led by NREL is working on using wind power to drive electrolysers that turn the ethanol’s CO2 by-product into e-fuels, explains Erik Ringle at NREL. A typical 50 million-gallon-per-year ethanol plant releases 14 tons of CO2, a natural by-product of … [Read more...]
EVs vs Biofuels: new study looks at ethanol’s impact on agricultural land use, food prices, emissions
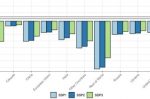
For transport, biofuels have lower emissions than gasoline/petrol, but EVs will have the lowest emissions of all. Hence the opposition to those biofuels, along with objections to the valuable cropland used to make the ethanol. But the overall advantage depends on the speed of transition to EVs charged with clean electricity. Now, a calculation has been made of the amount of agricultural land preserved for global food production - or kept as … [Read more...]
SAFFiRE: cheap, Sustainable Aviation Fuel from agricultural waste
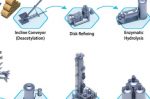
SAFFiRE (Sustainable Aviation Fuel From [i] Renewable Ethanol) is a 10-ton-per-day pilot plant project. The goal is 7bn gallons of sustainable, low-carbon aviation fuel by 2040. Ryan Horns at NREL explains that the sustainable fuel is made from corn stover, an agricultural waste product, chemically broken down into sugars that can then be converted to fuels. The SAFFiRE process can take advantage of the existing infrastructure of over 200 ethanol … [Read more...]
Converting captured CO2 directly into fuels could get simpler, cheaper
Converting captured CO2 directly into fuels (or other products) at scale seems an effective way to mitigate emissions. But most of the conversion methods, including electrochemical, thermocatalytic, photothermal, or photochemical processes, have not proved very effective. David Chandler at MIT describes how researchers there have identified the main stumbling block and found a very simple solution. Basically, at the molecular level, the contact … [Read more...]
Engineering yeast to create Biofuels from non-food crops (straw, grass, cellulosic waste)
Using ethanol can reduce the global consumption of fossil fuels. But, commercially, ethanol in the U.S. is produced from corn and not enough is grown to make a significant impact on U.S. fuel needs. Anne Trafton at MIT describes research that has engineered yeast to break down straw and woody plant material to create ethanol as efficiently as it’s done from corn. High yields of ethanol were extracted from five different types of cellulosic … [Read more...]
CCUS “gasphilic” process could double the conversion rate of CO2 into useful fuels
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is proving very expensive. So rather than simply store the CO2 underground it’s better to turn it into something that you can sell. Hence, much work is being directed at turning CO2 into transportation fuels or chemical feedstocks by focussing on the science of reactive materials: the other chemicals in the soup, using different catalysts, and even designing the right nanostructures to maximise the results. MIT’s … [Read more...]