Is bioenergy green? It depends, says Jessica Allen at the University of Newcastle. She lays out five key questions that should be asked about every bioenergy project. What is its source? Native forest residues, dedicated fast-growing biomass species, agricultural residues and “waste” biomass: all have pros and cons that must first be carefully measured. How many emissions are embodied in the collection and transport of the biomass to the plant? … [Read more...]
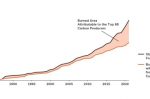
Evidence of a direct link between Wildfires and Fossil Fuel firms. Can it be used to sue them?
Wildfires are back in the news. The link to rising global temperatures caused by climate change is clear. Mark Specht at the Union of Concerned Scientists summarises their study that, for the first time, puts a number on the level of responsibility attributable to fossil fuel companies. Rising temperatures create a “vapour pressure deficit,” a measure of the power of the air to dry out plants and trees. That leads to an increase in the area … [Read more...]
Turning waste biomass into clean fuel: cheap, portable equipment, cuts emissions, earns income for rural poor
The burning of biomass accounts for 10% of primary energy used worldwide: wood, peat, animal dung, corn stalks, rice husks, hay, straw, and other agricultural waste. Billions of people, mainly in remote and poorer regions, rely on such fuels for cooking, heating, and other household needs. But it’s a major source of emissions as well as pollution. And, annually, an estimated $120bn worth of crop and forest residues are burned out in the open … [Read more...]
COP26: a strategy for tackling “imported deforestation”
Palm oil, beef, cocoa, coffee, soy, and other agricultural products are responsible for deforestation in the producing countries. Of the 10m hectares of tropical forest lost each year, two-thirds can be unambiguously attributed to agricultural expansion and international trade is responsible for about half of this. The EC is due in December to unveil a legislative proposal to address the issue. Alain Karsenty and Nicolas Picard, writing for IFRI, … [Read more...]
Sustainably harvested Forest Biomass can help replace coal and gas
Burning sustainably harvested wood pellets emits far less carbon than burning coal or gas. That’s the main reason why it should be used in the global energy transition, argues Jennifer Jenkins at Enviva. Coal is declining, but not fast enough. Gas consumption is rising. Forest biomass can more easily be swapped in than wind and solar to provide dispatchable power. But it must be done sustainably. Referencing her white paper, Jenkins sets out the … [Read more...]
Changes to national targets and forestry mean EC’s 55% plan is weaker than it looks
The EC’s plan to reduce the bloc’s emissions by 55% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels, instead of the previously agreed 40%, is very welcome but its implementation plan is flawed, says William Todts at Transport & Environment. The EU Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) won’t be enough on its own. So the plan allows nations to include “managing” forests and “tree plantations”, a big change because forests were not part of previous emissions … [Read more...]