How can we lower the lifetime emissions of building materials? Bernardino D’Amico at Edinburgh Napier University references his research to show how hemp-based materials can substitute for concrete. And it’s even more effective than timber, a popular low-carbon alternative. Growing industrial hemp can absorb twice as much CO₂ compared to growing trees. Raw hemp fibre can be processed into panels and mats for thermal or acoustic insulation. Hemp … [Read more…]
The benefits of Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines: omnidirectional, close-packed, easier to maintain + more
Most wind turbines are “horizontal axis,” pointing into the direction of the wind. “Vertical axis” turbines can capture wind energy from any direction, but current designs are less efficient and so get little attention and investment. Andrea Montanari at ECECP looks at innovative companies around the world that are trying to leverage the other advantages they have over the dominant horizontal versions. They are more stable (lower centre of … [Read more…]
EU ETS2 for Buildings, Road Transport in 2027: why we need auctions to start early
The EU has established a second emissions trading system (ETS) to put a carbon price on buildings and road transport, the “EU ETS2”. The ETS2 starts in 2027, but monitoring and reporting of ETS2 emissions will begin in 2025. One issue is that an ETS means prices for long-term fuel supply contracts will be affected, so a crucial question for firms is how to hedge their potential exposure, says Ingo Ramming at BBVA writing for the Florence School … [Read more…]
Infrared Fabric heat-emitting “wallpaper” avoids the disruption and expense of Heat Pumps
Hundreds of millions of buildings across the world need clean heating. But retrofitting them all for heat pump installation is going to be expensive, disruptive, and take a long time. Michael Siebert at Nottingham Trent University describes a completely different approach, using new high-tech infrared fabrics that emit heat. Made of graphene, they can be installed as easily as wallpaper. The radiated heat can be felt instantly, unlike the slow … [Read more…]
Buildings: how can Europe reduce emissions from Construction?
11% of global energy-related carbon emissions are embedded in the construction of buildings. Though focus has been on reducing operational emissions (28%, from heating and cooling, power etc.) there is not enough attention paid to construction, explains Carolina Kyllmann at CLEW. She looks at all the issues, including production of materials, transport to the site, construction, renovations, demolition and reuse of materials, and more. Kyllmann … [Read more…]
Electrostatic Generator fabrics can capture energy from cars depressing roads, swaying buildings + more
Literally anything that moves is using energy that can be harnessed. Not just waves rolling toward shore but cars depressing roads, buildings swaying in the wind, and much more. One way to harness it is to create a material that can be woven into the fabric of roads and buildings so that it captures the energy and converts it into electricity. Caitlin McDermott-Murphy at NREL describes research into Hexagonal Distributed Embedded Energy … [Read more…]
Geothermal Heat Pumps at scale avoid the cost of expensive long-distance transmission lines
A new analysis reveals that installing geothermal heat pumps in 70% of U.S. buildings can reduce the need for new long-distance transmission lines by 33%, explains Kelly MacGregor at NREL. The main message is that, though geothermal deployment is seen as expensive, the avoided costs are significant. Those transmission lines won’t be needed because geothermal is always local and can be deployed in both urban and rural places. Though the widespread … [Read more…]
EU ETS or national climate targets? We need both
The choice between using the EU ETS or national climate targets to decarbonise is a false dilemma. We need both, explains Chiara Corradi at T&E writing for the Florence School of Regulation. There are plenty of examples where a carbon market and national targets have delivered good results together, as in Germany, Finland, Denmark and Portugal. And, looking ahead over the next few decades, the right policies should be able to cope with ETS … [Read more…]
2024 a tipping point for Sustainable Buildings? Demand now outstrips supply in major cities
Guy Grainger at JLL, writing for WEF, believes 2024 will be the tipping point when returns for investing in sustainable office buildings will start to pay dividends for building owners. That’s because, according to JLL research, there is now a good premium on rents for sustainable buildings in important locations: just over 7% across eight cities in North America, around 10% across nine cities in the Asia Pacific and more than 11% in London. In … [Read more…]
2023: a year of climate backlash? Or a show of Europe’s green resilience
Looking at the mainstream media 2023 seemed to be a year of climate backlash, but the real story was Europe’s green resilience, writes William Todts at T&E. Though support in the German coalition for 100% electric vehicles by 2035 started to unravel, it didn’t: allowing combustion cars to keep running after 2035 on 100% e-fuels should change little given there’s no way such vehicles, if they ever get built, could compete with EVs, says Todts. … [Read more…]
EU Energy Outlook to 2060: power prices and revenues predicted for wind, solar, gas, hydrogen + more
Huangluolun Zhou, Elena Dahlem and Alex Schmitt at Energy Brainpool present their updated “EU Energy Outlook 2060”, modelling how the European energy system will undergo major changes in the coming decades while continuing to guarantee a secure supply and meet its climate targets. What do these developments mean for power prices, revenue potential and risks for solar PV and wind? The two main scenarios are “Central” and “GoHydrogen” for the EU 27 … [Read more…]
Thermal Energy Storage for heating and cooling Buildings: finding materials that melt at room temperature
Thermal Energy Storage (TES) in individual buildings can cut heating and cooling costs while delivering grid stability, explains Ryan Horns writing for NREL. Back in the 1800s blocks of ice were shipped to cities to cool buildings down. Today, research is underway to identify materials that can be heated or cooled by excess grid power and release or absorb heat when needed. Similarly, materials are being researched and developed that “phase … [Read more…]
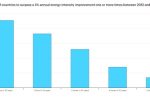
Annual Energy Efficiency improvements must double to meet climate targets. We know how to do it
Global energy intensity – a measure of how efficiently the global economy uses energy – improved by just over 2% in 2022. That needs to double to 4% annually to 2030 to meet global efficiency targets, explains Brian Motherway at the IEA. If achieved, by 2030 one unit of energy used will generate 40% more economic output than today. That’s huge, and shows why few other policy areas offer such widespread benefits. More than half of the 150 … [Read more…]
IRENA’s Innovation Week 2023: Renewable solutions to decarbonise end-use sectors
At the end of September IRENA held a four-day event “Innovation Week 2023: Renewable solutions to decarbonise end-use sectors” in Bonn, Germany. A wide range of speakers discussed tangible solutions to decarbonise energy intensive sectors such as transportation, buildings and industry, informed by first-hand project experiences and supported by insights from IRENA’s in-depth analyses. Topics included direct and indirect electrification, green … [Read more…]
Biosolar Roofs: solar panels mixed with vegetation can boost both power output and biodiversity
A biosolar roof is one that has installed both vegetation and solar panels on the top of a building. Does the presence of one obstruct the other, or do they in fact enhance each other? The answer is the latter, explain Peter Irga, Fraser Torpy, Eamonn Wooster, Charles Sturt, Robert Fleck at the University of Technology Sydney and Jack Rojahn at the University of Canberra who summarise their study. The vegetation cools the panels closer to their … [Read more…]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- …
- 9
- Next Page »