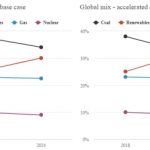
Carbon Brief’s Simon Evans runs through their analysis of the updated forecasts in the International Energy Agency (IEA) Renewables 2019 report, released this week. In its “base case” global renewable energy capacity will increase by 50% over 6 years. Rising from 2,501GW in 2018 to 3,721GW in 2024, it will add the equivalent of the entire US electricity system. In the “accelerated case” it’s 60%, further adding the equivalent of Japan’s. 85% of … [Read more...]
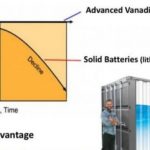
Can Vanadium Flow Batteries beat Li-ion for utility-scale storage?
It’s taken 40 years for lithium-ion battery technology to evolve into its current state, powering everything from the smallest electronic devices to Tesla’s 100MW battery farm in southern Australia. But utility-scale Li-ion batteries are rare. 99% of grid storage today is pumped hydro, a solution that will always be limited by geographical and environmental constraints. For utility-scale chemical batteries to take off they need a new technology, … [Read more...]
Cheaper than coal: IRENA’s comprehensive report on cost declines, all renewables categories
The International Renewable Energy Agency’s (IRENA) latest report Renewable Power Generation Costs in 2018 details the global weighted-average levelised cost of electricity (LCOE) for all commercially available renewable technologies. It states that renewables are already the lowest-cost source of new power generation in many parts of the world today. By as soon as 2020, onshore wind and solar PV will join hydropower in consistently offering a … [Read more...]
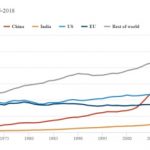
BP Review of 2018: record CO2, energy use as gas outstrips wind & solar
Energy use grew at 2.9% in 2018, the largest rise since 2010. It’s what happens when economies grow. But gas, oil and coal's contribution to that growth saw global CO2 emissions rise by 2% in 2018, the largest year-on-year increase in seven years. Wind and solar growth, driven by China though slowing in the US, EU, and India, achieved its second fastest rate on record - but still lagged behind gas additions. These are not the trends we need to … [Read more...]
2009 to 2017: solar, wind costs plummet, hydro steady, nuclear up
Between 2009 and 2017 prices dropped 76% for solar panels and 34% for wind turbines. Hydro and nuclear struggle to cut costs; as mature technologies, most of the efficiencies have already been squeezed out already. Also, they are difficult to productise and scale; dams (definitely) and nuclear plants (somewhat) are one-offs. In contrast, solar panels and wind turbines are far easier to productise and then mass produce. It’s why wind overtook … [Read more...]
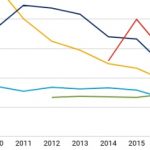
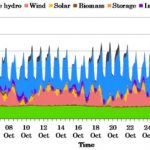
UK: Despite progress, 100% low-carbon is still a long way off
The UK transition is often cited as a success story. Coal’s contribution has dropped from 40% to 6%. Wind, solar and hydroelectric now generates more electricity than nuclear. Demand for electricity has also fallen. The carbon intensity of Britain’s electricity has almost halved, from over 500g of CO₂ per kilowatt-hour in 2006 to under 270g in 2018. The National Grid now expects to be able to operate a zero-carbon electricity system by 2025. But … [Read more...]
Greece: lignite asset sale failure could shift focus to electricity market reform and renewables
This month Greece’s Public Power Corporation (PPC) admitted its effort to sell a third of its lignite assets had failed. Dr. Nikos Mantzaris, of the think tank The Green Tank, gives his explanation for why the numbers never added up for the buyers. He now fears the PPC will simply sweeten the deal. Instead, Greece should abandon failing lignite assets, reform the electricity market and refocus on renewables. … [Read more...]
Electric metering should break its link with power consumed and create it directly with the costs of delivery
In a world where electricity is generated from non-renewables (oil, gas, nuclear) our meters measure and charge us for electricity delivered, as if it was a fuel being consumed. Going forward, the cost should be measured against what is actually being consumed. In a renewables world – particularly 'run-of-the-river' hydro, wind and solar - that’s not the electricity. It’s the wear and tear on the infrastructure. Treating these types of renewable … [Read more...]
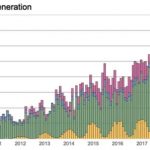
Britain has shifted 30% of its electricity away from fossil fuels in just nine years
Britain’s extraordinary energy transition is in part down to increased energy efficiency: put simply, less electricity was needed, whatever the source. But coal is still essential during spikes in demand. Given coal generation is due to be phased out by 2025, the country will need to find alternative power sources to cope during extreme weather events. And that overall decline in electricity demand is sure to be reversed as more vehicles and … [Read more...]