What is energy security? That’s what Maximilian Auffhammer at the Energy Institute at Haas asks and tries to answer, and he starts by saying what it is not and what solutions should not be used. Not importing won’t help because prices are global. “Energy security” can’t be taxed as an externality for much the same reason. Subsidising high prices for consumers decreases the value of energy efficiency investments. Instead, Auffhammer says the … [Read more...]
Avoiding renewables bottlenecks needs long term planning of electricity transmission infrastructure
As more renewables are rapidly added to grids, network operators must plan new transmission lines to integrate them immediately, avoiding wasteful bottlenecks. It’s a puzzle that’s getting bigger and more complex as the energy transition gains pace, which means transmission policy and planning must improve, and fast. Rather than making lots of small incremental steps, planning ahead will prove less costly and capture efficiencies and economies of … [Read more...]
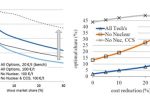
Will Wind & Solar confront its 10 challenges? If not, we need Nuclear, CCS, and more
Wind and solar’s impressive cost declines have seen its welcome and rapid emergence. But currently they account for a mere 2–4% of global energy. So these variable renewable energy sources (VREs) must now address 10 big challenges if they are to dominate the energy sector, explains Schalk Cloete in this data-led review. Their cost declines will be confronted and even cancelled by new costs they’ve not yet faced during their low-hanging-fruit … [Read more...]
DoE study: 45% of U.S. power from Solar by 2050. How?
This month, the White House released a U.S. Department of Energy report, the Solar Futures Study, on how solar power could generate up to 45% of the U.S. electricity supply by 2050. It’s less than 4% today. Joshua Rhodes at the University of Texas at Austin looks at what obstacles must be overcome. The good news is that the technology and engineering is already available. And solar’s advantage is that the sun shines nationwide. Other region and … [Read more...]
Can full-scale Distributed Solar really save $473bn in grid investments?
A giant model of the entire US electricity sector which captures distributed energy resource (DER) potential has been getting a lot of attention. It estimates that distributed solar and storage can save $473bn in system-wide costs when deployed at scale (enough to power more than 25% of US homes). Rooftop solar is definitely much more expensive than grid generation, but its location (on your own roof) avoids a range of costly transmission and … [Read more...]
Hydrogen: can gas, electricity and industrial majors agree on the next steps?
Here’s our written summary of our panel debate held on 16th June “Hydrogen: Designing the Net Zero Gas System”. With representatives from BASF, SNAM and ELIA to cover consumption, gas and electricity, there were plenty of differences of opinion. For example, with no end in sight for demand for green electricity for the grid, is it efficient to use some of it for hydrogen? Will subsidies for hydrogen skew markets away from industrial … [Read more...]
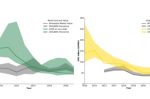
How to keep Wind and Solar profitable as its electricity gets cheaper
Success can cause problems. As wind and solar penetration increases the electricity it generates gets cheaper. If it stops being profitable we’ll stop building it, thus endangering our emissions-free goals. Dev Millstein at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory summarises their research paper that looks at how market value changed over time at 2,100 utility-scale power plants across major power markets in the U.S., using 2019 data. It’s clear … [Read more...]
Public opposition and grid integration costs: the two limiting factors for Wind?
Are we heading for an over-reliance on wind? With wind generation costs continuing to drop dramatically, Schalk Cloete takes a data-driven look at the obstacles wind will face as its contribution to the global energy mix (a little over 2% today) keeps rising. In the main, it is grid integration and public opposition to very visible turbines – and they are related. Putting turbines out of sight and offshore will increase transmission costs. And … [Read more...]
Rooftop Solar: economies of scale can challenge the centralised grid
One of our recent articles explained how rooftop solar PV is more expensive that a centralised supply, and that the transmission and distribution cost savings of the rooftop system, on their own, do not make up for this cost difference. Here, Javier López Prol at the Wegener Center for Climate and Global Change, University of Graz, responds to those challenges. First, the economies of scale of distributed rooftop solar are yet to be realised. … [Read more...]
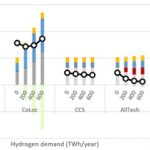
Green or Blue Hydrogen: cost analysis uncovers which is best for the Hydrogen Economy
Blue hydrogen is created from fossil sources, where the carbon emissions are captured and stored. Green hydrogen is made from non-fossil sources and favoured by policy makers who are wary of keeping the fossil economy going, even with CCS. As more regions commit to hydrogen, finding the right cost-optimal mix is crucial to its success. Schalk Cloete summarises his paper that models the whole system based on Germany. Integrating hydrogen will … [Read more...]
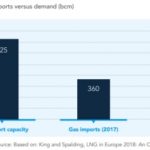
Europe has enough Gas infrastructure. Why build more?
In early November a first vote is expected in the European Parliament on the Recovery & Resilience Facility’s €672.5bn budget. Esther Bollendorff at CAN Europe runs through the arguments against providing any funding for new gas infrastructure. She presents evidence to show that the EU is already oversupplied with gas import capacity, and all new fossil gas transmission projects have been rejected by the market since 2017. Solar and wind … [Read more...]
Why promote Rooftop Solar when the Grid is so much cheaper?
Is rooftop solar in the U.S. getting more support than it deserves? One main argument from its advocates is that it will cut grid transmission and distribution costs that total hundreds of millions. Severin Borenstein at the Energy Institute at Haas crunches some numbers to try to uncover the true “avoided costs”. He shows that any savings won’t come even close to making up for the higher cost of rooftop electricity. It’s no match for the grid’s … [Read more...]
Norway’s power markets, storage and CCS plans can make it a decarbonisation hub for Europe
Though still heavily reliant on oil and gas, Norway can claim to be a central piece in Europe’s decarbonisation puzzle, explains Tshin Ilya Chardayre writing for the IFRI Centre for Energy & Climate. Norway’s substantial hydropower infrastructure gives it a reservoir storage capacity that could account for 10% of EU-wide energy storage needs by 2050. That would require international transmission cables and power markets, the development of … [Read more...]
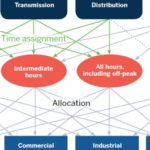
The new era of electricity needs modern ways to charge customers
Today’s technologies – wind, solar, storage - have widely differing cost and operating characteristics to fossil fuels. So the way customers are made to cover those costs – assigning different rates to different customer classes – should change. Jim Lazar and Mark LeBel at RAP explain why and how, referencing their comprehensive manual “Electric Cost Allocation for a New Era”. They describe how the full range of technologies now establishing … [Read more...]
Floating Solar: can it help ASEAN reverse coal’s continued rise?
Floating solar farms may be gaining traction in Asia. Capacity is still small: by 2019 the big players Japan and China had a combined floating photovoltaic (FPV) installed capacity of 1.3GW. But the ASEAN countries that had virtually nothing before 2019 now have over 51MW and have planned in another 858MW. A report by Sara Jane Ahmed and Elrika Hamdi at IEEFA explains why FPV is looking better and cheaper at balancing out peaks and troughs than … [Read more...]