The IEA has published “CO2 Emissions in 2022”, giving estimates of CO2 emissions from all energy sources and industrial processes globally. Emissions from energy combustion increased by 423 Mt, while emissions from industrial processes decreased by 102 Mt. Emissions from various sources (sector, fuel, region, heating, etc.) are broken down, with reasons for why the change happened. The report is part of the IEA’s first global stocktake of the … [Read more...]
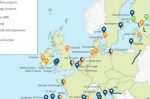
Germany: does the LNG infrastructure build-up deliver energy security or go too far?
A report out this month from the German government says it wants a significant “safety buffer” of new LNG import capacity, to ensure that the country - and neighbouring landlocked states - will receive sufficient supply of natural gas in the coming years. It says an overcapacity is needed in case of failures due to accidents, sabotage or other external factors not under German or EU control. Events have shown that unilateral dependencies in … [Read more...]
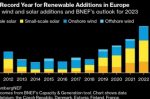
EU: data shows Russia–Ukraine war has not increased Coal and emissions. It’s quite the opposite
The Russian gas crisis has not resulted in the return of coal and high emissions in Europe, says Lauri Myllyvirta at CREA. He presents the figures that show quite the opposite. Coal returned, as expected, with the post-Covid rebound, but peaked in September 2022 below its pre-Covid level, and has been falling since along with emissions. Meanwhile, high gas prices caused by Russia’s cut-off has kept gas demand low and, more importantly, driven the … [Read more...]
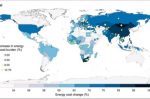
Russia–Ukraine war: household energy costs worldwide have nearly doubled, with the poorest hit hardest
A new study measures the effect of the Russia-Ukraine war on household energy costs worldwide. It’s nearly doubled, explain Klaus Hubacek, Jin Yan and Yuru Guan at the University of Groningen and Yuli Shan at the University of Birmingham. Their study sums the costs of direct energy like heating, cooling, lighting and mobility, as well as the indirect costs through the energy used to produce goods and services. That doubling translates into an … [Read more...]
Will Europe now commit to long term imports of large quantities of LNG?
The EU and European nations need a more secure LNG supply strategy than just buying on the spot market where there is little control of prices and quantities. With Russian gas off the agenda for the foreseeable future, it’s LNG that’s filled the gap. But spot prices have been extremely high, and may return to the same heights. And though China’s Covid-caused drop in LNG consumption helped enable Europe to buy enough for now, that won’t be the … [Read more...]
Coal phase-out: Developing world targets are unfeasible. Rich nations must cut emissions faster
Developing nations like China, India and South Africa are being asked to phase out coal more than twice as fast as any comparable energy phase-out in history, for the world to meet the Paris climate goals. That’s simply unrealistic say James Price and Steve Pye at UCL who present the results of their new study. Instead, rich nations will have to reduce significantly their oil and gas to compensate for the shortfall. An oil and gas peak isn’t good … [Read more...]
Big Consultancies are now advising on climate change. Will it conflict with their business-as-usual work?
The world’s top management consultancies - like BCG, Accenture, PwC, EY, McKinseys - who for decades have advised the biggest polluters, are now rushing into the business of helping companies cut emissions to become more sustainable, explains Emma Thomasson at Clean Energy Wire. The necessary expertise is in very short supply, so they are retraining staff, poaching environmental experts, and buying up smaller specialist firms. BCG is even running … [Read more...]
Gas: a history of Energy Security in the EU. And what’s next post-Russia?
The security of supply of gas has been the hottest topic of the last 12 months since Russia invaded Ukraine. James Kneebone at the Florence School of Regulation (FSR) has written an explainer that lays out the EU’s history of dealing with energy security, going back to the 1990s. Because the EU has a single market for natural gas and widely shared value chains (pipelines, LNG terminals, storage, etc.), impacts are felt across the bloc. But that … [Read more...]
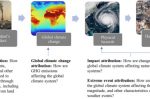
How new and better science is driving climate litigation
Delta Merner at the Union of Concerned Scientists makes her predictions for climate litigation in 2023. There will be much more, globally. The stand out observation is that new and better science is driving the evidence, impacting the litigants and the courts. That points at major changes to the litigation landscape. More granular geographical evidence allows local litigants to more accurately make a case for connecting emissions and pollutants … [Read more...]
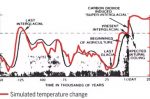
What if Exxon had acted on its 1970s climate forecast? No climate crisis, cheap energy, Exxon the unrivalled top global energy firm
In January the world media widely covered a paper published in Science that looked at the internal Exxon report that predicted the climate change crisis we now all know we are facing. The paper concludes that the Exxon forecasts were very accurate. John Grant at Sheffield Hallam University composes a counterfactual history of what would have happened in Exxon and the world had taken the report seriously and acted immediately. Yes, we’d have … [Read more...]
Message to environmentalists and the left: you can’t oppose both fossil investments and Carbon Pricing
Environmental and social justice opponents of fossil investments need to think carefully about the consequences of preventing all forms of new fossil infrastructure and maintenance. As Catherine Wolfram at the Haas School of Business explains, if fossils are phased out faster than clean energy is phased in, consumer prices go up and the fossil firms profit. A carbon price – often opposed by the same U.S. “progressives” as a tax disproportionately … [Read more...]
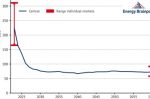
EU Energy Outlook to 2060: how will power prices and revenues develop for wind, solar, gas, hydrogen + more
Alex Schmitt and Huangluolun Zhou at Energy Brainpool present a summary of their “EU Energy Outlook 2060”. Its scenarios map out how the European (EU 27, UK, Switzerland and Norway) energy system will change dramatically in the coming decades. Current geopolitical tensions are added to climate mitigation and an outdated power plant fleet as the main drivers of change at the EU and national levels. The in-depth modelling is trying to answer the … [Read more...]
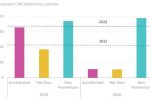
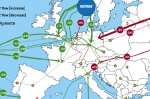
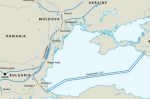
EU gas post-Russia: out-of-date regulations are preventing new gas flows from west to east, not infrastructure
### REGISTER NOW ### for our vitally important 2-panel event “The Energy Crisis and Russian Aggression Against Ukraine – Key Challenges for the Central European Energy Sector”, on Thursday December 8, 13:00 – 17:00 CET (Address: Rue Belliard 40, 1040 Brussels). High-profile confirmed speakers include Kadri Simson, European Commissioner for Energy, EC; Leszek Jesień, Chairman of the Board, CEEP; Jerzy Buzek, MEP and former president of the … [Read more...]
What was Europe’s dependence on gas prior to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine?
### REGISTER NOW ### for our vitally important 2-panel event “The Energy Crisis and Russian Aggression Against Ukraine – Key Challenges for the Central European Energy Sector”, on Thursday December 8, 13:00 – 17:00 CET (Address: Rue Belliard 40, 1040 Brussels). High-profile confirmed speakers include Kadri Simson, European Commissioner for Energy, EC; Leszek Jesień, Chairman of the Board, CEEP; Jerzy Buzek, MEP and former president of the … [Read more...]
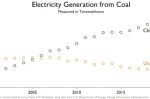
IEA says peak coal is a few years away, but China’s demand for energy suggests not
Lucas Davis at the Haas School of Business questions the IEA’s optimism revealed in its latest World Energy Outlook 2022 that predicted coal will peak in the next few years. In 2021, global coal consumption increased 5% and global electricity generation from coal reached an all-time high. China is the main driver - last year over half of all coal-fired electricity generation came from China - and its energy demand keeps rising. Between 2000 and … [Read more...]
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- …
- 54
- Next Page »