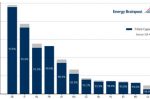
Prices on the European gas market have fallen sharply since August 2022 and Europe’s gas storage facilities are almost full. That’s good news, but the problems aren’t over. Simon Göss at cr.hub, writing for Energy Brainpool, explains why by looking at the data. He runs through the main factors driving the changes, primarily strong LNG imports, Norway’s increased production, mild weather, and lower gas consumption (particularly in industry). … [Read more...]
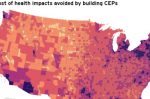
Pollution costs are driving U.S. states to look for alternatives to Gas-Fired Plants
In the U.S. a growing number of states and regulators are directing utilities to look for alternatives to proposed gas-fired power plants, citing environmental justice and community health impacts, explain Caitlin Odom and Lauren Shwisberg at RMI. So it’s not just about emissions: pollution matters too. The authors quote studies that show clean energy portfolios (CEPs) not only reduce energy costs, but can save billions of dollars in community … [Read more...]
Event Summary: “CHINA: Carbon Neutral by 2060 – The Future of Gas”
Here are the written highlights of our 2-day 4-session workshop “CHINA: Carbon Neutral by 2060 – The Future of Gas”, compiled by Helena Uhde at ECECP. Here you can quickly see the main points made by our expert panellists. Global events have made gas the hottest of issues, and the implications for both Europe and China are strongly reflected in all the sessions. The four session topics were Security of Supply, CCUS for the Gas Sector, Competitive … [Read more...]
Europe’s decoupling of electricity and gas prices: the crisis is temporary, so why do it?
The debate is intensifying over how to decouple power prices from the extraordinarily high natural gas prices in Europe. Simona Benedettini and Carlo Stagnaro warn that the current problem of high prices is not caused by the mis-functioning of electricity markets, but by the exceptional trend in gas prices. So should the markets be re-designed at all? Will we lose the benefits of the current design, one being the reliable profits that renewables … [Read more...]
$78tn net gain for compensated global Coal phase-out, when social benefits are added
Is replacing coal with renewables too expensive? No, it’s the opposite, explain Tobias Adrian at the International Monetary Fund, Patrick Bolton at Imperial College London and Alissa Kleinnijenhuis at the Oxford Martin School who summarise their paper. When the social benefits are added, the net gain globally is around $78tn under a conservative estimate. That’s equal to 1.2% of current world GDP every year until 2100 – these are real economic … [Read more...]
Fossil fuel producers can decarbonise by exporting Electricity, Hydrogen, and Steel
The compelling reason why fossil fuel producers will be needed even beyond 2050 is that they currently provide over 80% of global energy, and 90% of the world’s population still needs the wealth creation that energy delivers, says Schalk Cloete. Given that, he summarises his co-authored paper that takes a close look at how a fossil exporter, Norway, can trade with an importer, Germany, while decarbonising. The modelling focusses on electricity … [Read more...]
As spot market electricity prices break all records, what is the prediction for winter?
Spot market prices for electricity have been breaking all records, as European leaders and their ministers intensify their discussions on how to deal with the crisis. Simon Göss at cr.hub, writing for Energy Brainpool, starts by explaining how the markets work, noting that price rises are indeed being driven by fossil prices and not CO2 certificates. Göss looks at how prices have climbed in Germany, France, the Baltics and Spain, and how the … [Read more...]
Don’t cap gas prices for consumers. It won’t reduce demand. Instead, subsidies must reward cuts in gas use
European nations are considering capping the price of gas that consumers pay, a subsidy that governments will pay for, to ensure households don’t freeze this winter. Daniel Gros at CEPS warns that this strategy will remove the incentive for consumers to cut their gas use, keeping international market prices high. Instead, governments should incentivise a reduction in gas use. Gros has modelled two strategies. The first is to pay households for … [Read more...]
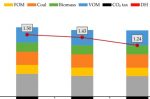
A role for Coal? Low-cost, negative emissions Blue Hydrogen from “MAWGS” Coal/Biomass co-gasification
Schalk Cloete summarises his co-authored study that explains how to make hydrogen at unbeatably low prices from coal/biomass co-gasification. Though the “blue” hydrogen process creates CO2, the self-contained plant using a membrane-assisted water-gas shift (MAWGS) reactor means 100% is captured easily. Better still, the use of biomass means the plant achieves negative emissions. The overall efficiency of the process is a very impressive 69%. The … [Read more...]
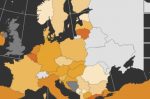
If Russia cuts off its gas supply can we achieve EU storage targets for winter?
Calvin Triems at Energy Brainpool summarises their analysis of whether and how Europe can achieve its storage targets for 2022. There are four scenarios: “Base Case”; “Nordstream@40%” where there’s no change to Russia’s mid-June gas flow cut to 40%; “Nordstream@40% + No Freeport” where the unexpected fire in early June at the U.S. Freeport LNG terminal remains unresolved for months; “Nordstream@0% + No Freeport” where Russia cuts off supply … [Read more...]
Methane emissions reach unexpected new highs. Is climate change causing a runaway effect?
Simon Redfern at Nanyang Technological University, Singapore summarises his co-authored study that says methane emissions are four times more sensitive to climate change than that estimated in the latest IPCC report, which was only published in February 2022. The study follows the observation that, despite the pandemic stalling the world economy, methane emissions have reached new highs. Not because methane emissions have risen but because … [Read more...]
Will price caps on Russian oil work? Three experts debate
Whatever the G7 does, the objective is to cut revenues flowing into Russia, not oil flowing out. And whatever the sanctions, getting compliance from neutral and pro-Russian countries will need a strong positive incentive. Hence the idea of a price cap which would keep prices low. Here, three experts – Edward Fishman and Brian O’Toole at the Atlantic Council, and Mark Mozur at S&P Global Commodity Insights (with background by Atlantic … [Read more...]
Imposing a $50/barrel tariff on Russian oil is the best sanction
Is there a way to impose sanctions on Russia that cuts its revenues without causing fossil fuel prices to balloon? The current strategy has seen oil prices rise to $120/barrel by mid-June, so although volumes are down Russia has seen no reduction in revenues. In other words, it has not achieved its objective, says Edward Chow at the Center for Strategic and International Studies. Instead, he argues for imposing a big import tariff – like … [Read more...]
If Russia cuts its gas supplies to Germany, what happens next?
Replacing Russian pipeline gas to Europe in the short term is much more difficult than finding alternative sources for coal and oil. It’s why the EU hasn’t banned Russian gas. But what if Russia cuts off the supply? Benjamin Wehrmann at Clean Energy Wire looks at what the consequences and options are for Germany. Though Germany aims to wean itself off Russian supplies almost entirely by 2024, a sudden cut would have serious consequences. Storage … [Read more...]
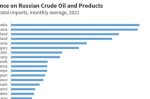
EU’s latest sanctions on Russian Oil: what are they and will it work?
On June 3, the EU agreed an embargo on Russian crude oil and petroleum products. Ben Cahill at the Center for Strategic and International Studies looks at the details of the latest sanctions imposed in response to Russia's ongoing invasion of Ukraine, and assesses the possible consequences. The aim is to cut oil imports from Russia by 90 percent by February 2023. A critical part of the sanctions is a ban on providing shipping insurance to Russian … [Read more...]
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- …
- 54
- Next Page »