The industrial sector throughout the world needs to decarbonise. At the same time, no one country wants to incur the costs and risk losing market share to rivals who decarbonise slowly (or not at all!) Hence the EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) that imposes costs on carbon-intense imports. This protects clean EU industries while incentivising importers to get going with decarbonisation or lose their European customers. Allegra Dawes … [Read more...]
It’s time to sanction Rosatom subsidiaries, part of Russia’s LNG production chain
Following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, the West and its allies imposed a series of sanctions to cut dependence on Russian oil and gas imports, as well as hit Russian import earnings. Ihor Moshenets at the Central European University points to a serious sanctions blind spot: Rosatom, Russia’s nuclear major. Rosatom has avoided sanctions because it is ostensibly a nuclear technology provider, with long term commitments to Europe that do not … [Read more...]
New Concentrated Solar Power system delivers 1,000°C for industrial processes + more
Zach Winn at MIT describes a new method of building high-temperature concentrated solar power systems. The solar receiver heats air to around 1,000°C at atmospheric pressure. The system circulates the hot air with no combustion or emissions to drive a turbine. The system can deliver daytime power and overnight thermal energy storage to provide round-the-clock power. More interestingly, it can provide industrial-grade heat. It’s being … [Read more...]
Are the prospects for Small Modular Reactors being exaggerated? Five key characteristics examined
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) are being presented as the next generation of nuclear technology. While traditional plants face cost overruns and safety issues, SMRs are seen by their champions as cheaper, safer, and faster to deploy. But Ed Lyman at UCS cites evidence that cast these claims into doubt. In five sections of this article, he lists the reasons why. SMRs are not more economical than large reactors. SMRs are not generally safer or more … [Read more...]
China’s plans for large-scale Offshore Solar
If offshore wind, why not offshore solar? It’s been talked about for a while and implemented on a small scale in places like Norway. You Xiaoying, writing for Dialogue Earth (formerly China Dialogue), looks at China’s efforts to establish it as a new and – once scaled up - major contributor to the energy transition. The main advantages over land-based solar are clear: large spaces of land must be found, they’re not usually near population or … [Read more...]
Hydrogen too expensive for Trucking? 85% of the cost is getting it to the pump
Hydrogen can be a clean fuel for heavy duty trucking. The target price for rapid adoption is $4-$5/kg, yet right now hydrogen costs $13-$16/kg at refuelling stations in California. Cutting the cost of making the hydrogen is proving slow. But Ted McKlveen and Bav Roy at Verne, writing for WEF, show that the production only accounts for 15% of the cost at the pump. Roughly 50% of the cost is from running the pump station (equipment like compressors … [Read more...]
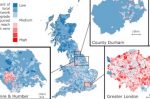
Upgrade the grid, or avoid by incentivising flexibility? Electricity demand mapping can tell you what to do
Power grids across the world need upgrading to accommodate the rapidly rising amount of electricity being generated. Without it, it is a serious bottleneck to the transition to clean fuels. Sheridan Few at the University of Leeds summarises his co-authored study that creates a map of where upgrades are most needed in the UK. The map’s purpose is twofold. Firstly, it predicts where power consumption will rise the most and the upgrades are … [Read more...]
58 national Hydrogen strategies published: a step forward, but importers’ and exporters’ plans still need to match up
So far, 58 national hydrogen strategies and roadmaps have been published. Anne-Sophie Corbeau and Rio Kaswiyanto at the Center on Global Energy Policy take a close look, summarising their regularly updated database, the “National Hydrogen Strategies and Roadmap Tracker.” Only 12 countries are planning to become importers, mostly in Asia and Europe. Most of the others plan to be exporters. Many existing fossil fuel exporters want to preserve their … [Read more...]
Financing Hydrogen projects in Emerging Markets and Developing Countries
Financing the new hydrogen economy is already a challenge. Financing hydrogen production in Emerging Markets and Developing Countries (EMDC) is an even bigger one, yet vitally important for supplying richer nations with hydrogen while creating new industries in the EMDC. This month, the World Bank Energy Sector Management Assistance Program (ESMAP) together with the Government of the Netherlands and Invest International organised a Financing … [Read more...]
Zero-Emission Trucks can be cost competitive by 2035 (and much sooner depending on size and range)
Zero-emission medium- and heavy-duty vehicles (MHDVs) such as battery electric and hydrogen fuel cell electric, in every size and range category, can be cost competitive with their diesel equivalents by 2035. In several of those categories it can be much sooner – within the next six years - explains Julia Thomas at NREL. Researchers there have modelled how the total cost of driving for zero-emission and diesel MHDVs can evolve over time under … [Read more...]
How to handle rapid Grid load growth: Data Centres can set the template for EVs, Buildings, new Industry
Due to their growing power demand, data centres can set a precedent for how to handle rapid load growth in a way that supports the grid and ensures reliable, resilient, carbon-free electricity. In other words, they can set the template for the coming surges in demand from EVs, buildings electrification, and the new rich-world policies of onshoring industry and manufacturing, explain Alexandra Gorin, Roberto Zanchi and Mark Dyson at RMI. Big, … [Read more...]
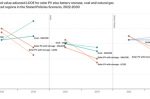
A global review of Battery Storage: the fastest growing clean energy technology today
The IEA report “Batteries and Secure Energy Transitions” looks at the impressive global progress, future projections, and risks for batteries across all applications. 2023 saw deployment in the power sector more than double. Strong growth occurred for utility-scale batteries, behind-the-meter, mini-grids, solar home systems, and EVs. Lithium-ion batteries dominate overwhelmingly due to continued cost reductions and performance improvements. And … [Read more...]
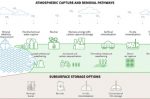
Carbon Dioxide Removal: here’s what the start-ups want from policymakers, partners
The scaling up of a global carbon dioxide removal (CDR) industry is facing significant challenges over proven results and therefore funding. Guy Wohl and Emily Rogers at RMI have interviewed the CEOs of four start-ups who feature in RMI’s Applied Innovation Roadmap (AIR) report for CDR. “Rewind” is developing a biogenic CDR (bCDR) approach that sinks forestry residual plant matter in the Black Sea to store the plant-embedded carbon for centuries. … [Read more...]
Big Data’s huge power demand can migrate globally, instantaneously: implications for planning regional capacity and markets
Something is going to make the planning of regional power generation and associated markets even harder: the ability of big data users to shift their demand across the globe quickly, based on price. Ira Joseph at CGEP peers into the near future to ask some difficult questions. When such power demand can “at the push of a button” migrate long distances, how do you make predictions for local capacity needs? And today, market design in most … [Read more...]
Hemp-based building materials: a low-carbon substitute for timber, concrete
How can we lower the lifetime emissions of building materials? Bernardino D'Amico at Edinburgh Napier University references his research to show how hemp-based materials can substitute for concrete. And it’s even more effective than timber, a popular low-carbon alternative. Growing industrial hemp can absorb twice as much CO₂ compared to growing trees. Raw hemp fibre can be processed into panels and mats for thermal or acoustic insulation. Hemp … [Read more...]
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- …
- 199
- Next Page »